Optimization of Potassium Carbonate-based DES as Catalyst in the Production of Biodiesel via Transesterification
Keywords:
deep eutectic solvent, fatty acid methyl ester, Jatropha curcas oil, potassium carbonate, transesterificationAbstract
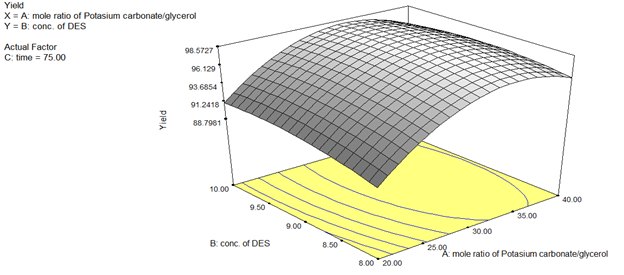
Increasing energy demand necessitates the production of sustainable fuels, which can be in the form of bio-fuels. One of such bio-fuels is biodiesel, which is typically produced via transesterification. The development of homogeneous catalyst that is relatively easy to synthesize, cheap, reusable, and environmentally friendly, is a major issue in transesterification reaction. The use of Deep eutectic solvent (DES) as catalyst, is believed to be a significant step in the direction of attaining a sustainable bio-economy. In this study, deep eutectic solvent was synthesized from different mole ratios of K2CO3/glycerol. The synthesized DES was used as catalyst in the transesterification reaction to produce biodiesel from Jatropha curcas oil. Box-Behnken design (BBD) was used to determine the factors that significantly affect the biodiesel yield. Optimum fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) yield of 98.2845% was achieved at optimum conditions of 1:32.58 mole ratio of K2CO3/glycerol, 8.96% w/w concentration of DES, and 69.58 minutes. GC-MS analysis revealed that the produced biodiesel contained 98.87% ester content. The properties of the biodiesel produced were characterized and found to agree with those of ASTM D6751-12 standard. Thus, suggesting the synthesized DES is a promising catalyst in the transesterification reaction to produce biodiesel from Jatropha curcas oil.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Abdulwasiu Abdurrahman, Saidu Muhammad Waziri, Olusegun Ayoola Ajayi, Fadimatu Nyako Dabai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Selvaraju Sivamani, Marwan Ahmed Sulieman Al Aamri, Aseela Musalem Awad Anthroon Jaboob, Azeezah Mohammed Masoud Kashoob, Layal Kamall Abdullah Al-Hakeem, Mouna Salim Mhaad Said Almashany, Muna Ahmed Mohammed Safrar, Heterogeneous Catalyzed Synthesis of Biodiesel from Crude Sunflower Oil , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- C. B. Adindu, S. C. Nwanonenyi, C. B. C. Ikpa, Experimental and computational studies of the corrosion inhibitive effects of Zingiber officinale rhizomes on mild steel corrosion in acidic solutions , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 3, August 2023
- E. E. Etim, Benchmark Studies on the Isomerization Enthalpies for Interstellar Molecular Species , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 2, May 2023
- David O. Adekunle, Esther O. Faboro, Labunmi Lajide, Identification and quantification of bioactive compounds indifferent extracts of morinda lucida benth (rubiaceae) root using GC–MS analysis , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- S. E. Shaibu, E. J. Inam, E. A. Moses, U. A. Ofon, O. K. Fatunla, C. O. Obadimu, N. D. Ibuotenang, N. O. Offiong, V. F. Ekpo, T. J. Adeoye, E. L. Udokang, D. P. Fapojuwo, Prospects of nanosorption and photocatalysis in remediation of oil spills , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- A. E. Ibor, D. O. Egete, A. O. Otiko, D. U. Ashishie, Detecting network intrusions in cyber-physical systems using deep autoencoder-based dimensionality reduction approach anddeep neural networks , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Terver Daniel, F. Eriba-Idoko, J. O. Tsor, S. T. Kungur, E. O. Enokela, F. Gbaorun, E. C. Hemba, A. A. McAsule, N. S. Akiiga, P. O. Ushie, Effects of Repeated Frying on Physical Properties of Cooking Oil obtained from Local Markets in Makurdi Metropolis, Benue State, Nigeria. , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- Chidi Duru, Ijeoma Duru, Chiagoziem Chidiebere, Virtual Screening of Selected Natural Products as Human Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 Blockers , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- Paul Tawo Bukie, Idongesit E. Eteng, Eyo E. Essien, Development of internet of things-based petroleum pipeline topology leak monitoring and detection system using sensors , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- K. K. Adama, I. B. Onyeachu, The corrosion characteristics of SS316L stainless steel in a typical acid cleaning solution and its inhibition by 1-benzylimidazole: Weight loss, electrochemical and SEM characterizations , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 2, May 2022
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






