Theoretical Investigation of Diameter Effects and Edge Configuration on the Optical Properties of Graphdiyne Nanotubes in the Presence of Electric Field
Keywords:
Graphdiyne nanotubes, Electric field, Band gap, Optical properties, SIESTA code, Density functional theoryAbstract
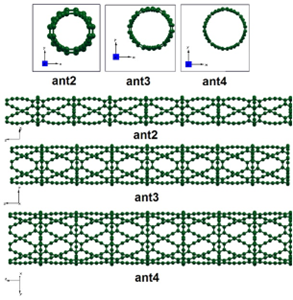
In this research, the structural, electronic and optical properties of the armchair (ant) and zigzag (znt) Graphdiyne nanotubes (GDY-NT) with different diameters were studied based on density functional theory (DFT). The computations were done using SIESTA code, based on linear combination of localized atomic orbitals (LCAO) method and the generalized gradient approximation (GGA). The results from the band structure analysis show that all these nanotubes are semiconductor with direct band gap at gamma point. The band gap of the nanotubes is clearly dependent on the nanotube diameter, and by increasing the nanotube diameter, the band gap is decreased. Optical properties such as dielectric function; absorption coefficient, optical conductivity and refractive index were examined and calculated for all samples. The results show that all these functions have an inverse relationship with the nanotube diameter and a direct relationship with the band gap. The effect of applying the external electric field with intensity of 0.1 V/Å, 0.2 V/Å in the direction of x-axis (perpendicular to the nanotube axis) on the structural and electronic features of these nanotubes has been studied and calculated.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 T. M. J. Abdulkadhim, S. A. A. Alsaati, M. H. Shinen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







