Effects of different electrolytes on the structure and yield ofgraphene oxide produced via electrochemical exfoliation
Keywords:
Graphene, electrochemical exfoliation, electrolyte, quality, yield/production rate, graphiteAbstract
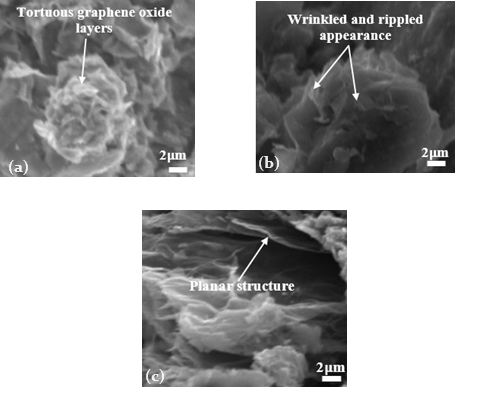
The most suitable electrolyte for graphene oxide synthesis, in terms of both production efficiency and quality, using the electrochemical exfoliation technique has been investigated and reported in this study. Simultaneous anodic and cathodic graphene oxide production using ten (10) different electrolytes, including acids (H2SO4, HCl, HNO3), bases (KOH, Ca(OH)2, Mg(OH)2, NaOH), and salts (NaCl, (NH4)2SO4, K2SO4), was studied under the same experimental conditions of bias voltage, graphite nature, exfoliation time, electrolyte molarity, and post-exfoliation treatments. Assessment of the graphene oxide structures and production rates was supported using Raman spectroscopy, high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HRSEM), and EDS (energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy), attached to the scanning electron microscope. Analysis of the results obtained reveals that H2SO4 showed the highest graphene oxide yield (86%) but with comparably low graphene oxide quality in terms of defect concentration, presence of oxygen functional group contamination, and crystallite properties. The aqueous NaCl, Ca(OH)2 and Mg(OH)2 electrolytes did not show any graphene oxide exfoliation effect. However, from the series of electrolytes examined, aqueous (NH4)2SO4 exhibited an excellent combination of efficient graphene oxide yield and high-quality characteristics due to its relatively high yield of 74% and superior quality of the produced graphene oxide with the comparatively lowest defect density, ?D, and highest C/O (carbon-to-oxygen) ratio. The tortuous, agglomerated, and planar layers of the distinct 2D graphene oxide sheets were also clearly revealed by the SEM images. In essence, the roles played by dissociated sulfate (SO42?), nitrate (NO32?), chlorides (Cl?), and hydroxides (OH?) ions in the series of complex electrochemical reactions toward the intercalation, exfoliation, yield, and properties of graphene oxide produced are discussed. From the series of electrolytes tested, aqueous (NH4)2SO4 emerged as the most relatively suitable electrolyte for the synthesis of graphene oxide because it combines both high yield and fine quality.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Oluwole Adigun, Lasisi Egibunu Umoru, Temidayo Nancy Iwatan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Olayinka Oluwaseun Oluwasina, Mochamad Zakki Fahmi, Olugbenga Oludayo Oluwasina, Enhancing cellulose fiber properties from chromolaena odorata and anana comosus through novel pulping chemical mixtures , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- K. Manickavelan, S. Ahmed, K. Mithun, P. Sathish, R. Rajasekaran , N. Sellappan, A review on Transforming plastic wastes into fuel , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- N. D. Umar, O. V. Omonona, C. O. Okogbue, Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Multivariate Analysis and Water Quality Index in some Saline Fields of Central Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- Tertsea Igbawua, Martha Hembafan Gbanger, Fanan Ujoh, Suitability Analysis for Yam Production in Nigeria using Satellite and Observation Data , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Abdulwasiu Abdurrahman, Saidu Muhammad Waziri, Olusegun Ayoola Ajayi, Fadimatu Nyako Dabai, Optimization of Potassium Carbonate-based DES as Catalyst in the Production of Biodiesel via Transesterification , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Odilon Joseph TOWANOU, Hagninou Elagnon Venance Donnou, Gabin Koto N’Gobi, Augustin Enonsi Leode, Basile Kounouh´ewa, Solar Energy Storage by Fuel Cell Technology at Abomey-Calavi (Benin) , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 2, May 2023
- K. M. Omatolaa, A. D. Onojah, A. N. Amah, I. Ahemen, Synthesis and characterization of silica xerogel and aerogel from rice husk ash and pulverized beach sand via sol-gel route , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- Mahouton Justine Carine ADJASSA, Gabin KOTO N'GOBI, Hagninou Elagnon Venance DONNOU, Clément Adéyèmi KOUCHADE, Basile Bruno KOUNOUHEWA, Generation of Electricity From a Hydraulic Turbine in the Djonou River (Benin) , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 2, May 2023
- K. O. Sodeinde, S. A. Animashaun, H. O. Adubiaro, Methods for the Detection and Remediation of Ammonia from Aquaculture Effluent: A Review , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Elsammani Ali Shokralla, Improving the thermal stability and dielectric properties of epoxy/phenolic resin type (novolac) composites by incorporating carbon nanofibers (CNFs) , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 1, February 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






