Theoretical Study on 10C Elastic Scattering Cross Sections Using Different Cluster Density Distributions and Different Potentials
Keywords:
Elastic scattering, density distribution, Optical model, cluster model.Abstract
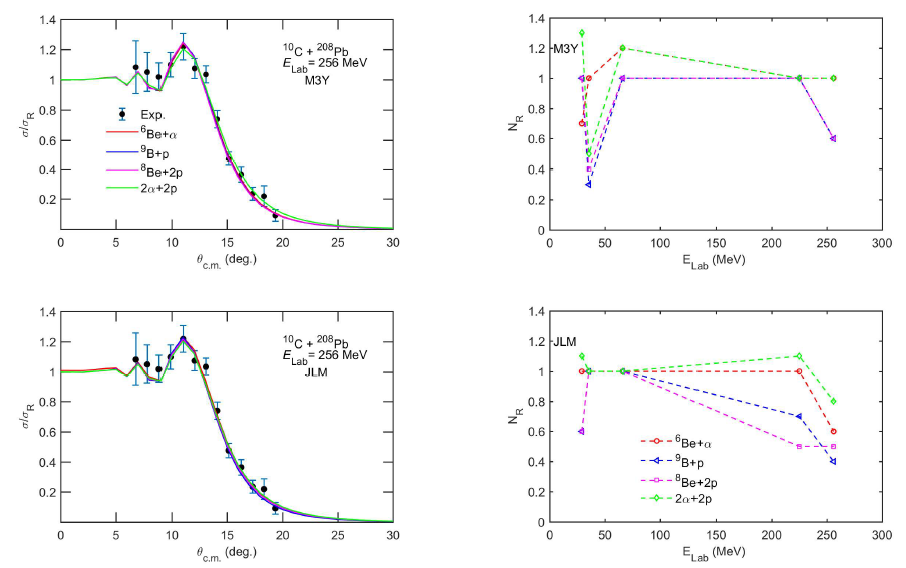
Elastic scattering cross sections are a fundamental aspect of nuclear physics research, and studying the cross sections of various nuclei can provide important insights into the behavior of nuclei. In this study, the elastic scattering cross sections of 10C projectile by 27Al, 58Ni, and 208Pb target nuclei are analyzed. The aim of this study is to investigate the cluster structure of 10C and the sensitivity of the elastic scattering cross sections to different potentials. To achieve this objective, the double folding optical model and a simple cluster approach are used to analyze the cross sections. The real part of the optical potential is obtained by folding two different effective interactions, Michigan-3-Yukawa (M3Y) and JeukenneLejeune-Mahaux (JLM), with four different cluster density distributions of the 10C nucleus: 6Be + \alpha, 9B + p, 8Be + p + p, and \alpha + \alpha + p + p. The imaginary part is taken to be a Woods-Saxon phenomenological form. The sensitivity of the elastic scattering cross sections to different potentials is assessed by comparing the results obtained using different potentials. The cluster structure of 10C is validated by comparing the theoretical results with experimental data. The results show that the cross sections are sensitive to the choice of potential used and that the cluster structure of 10C is validated. The theoretical results show reasonable agreement with the experimental data.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Sunday Olorunfunmi, Armand Bahini, Adenike Olatinwo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






