Health risk evaluation of radon progeny exposure in Nigerian traditional mud houses
Authors
-
Kehinde Aladeniyi
Department of Physics, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria
Abstract
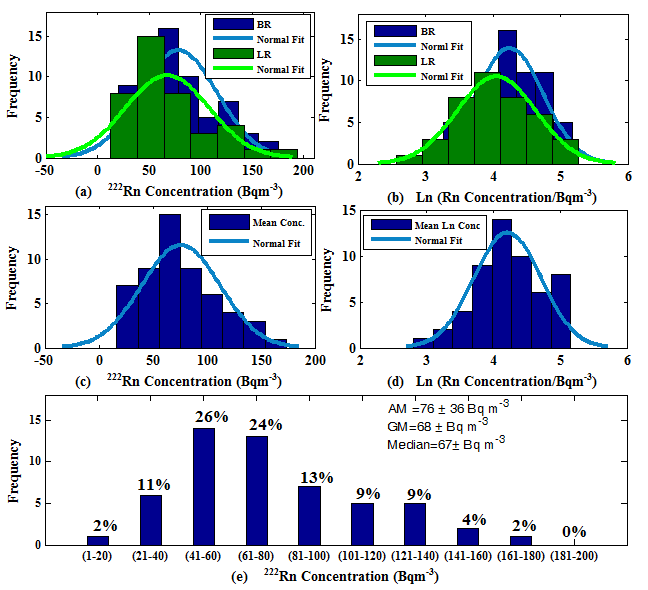
In a study of 56 randomly selected Traditional Mud Houses (TMHs) in Nigeria, the radiation health impacts of radon progeny were evaluated using CR-39 radon detectors within a rainy season. The measured radon concentration ranged from 17 to 174 Bq m-3, with an average value of 76 Bq m-3 (SD = 36). This was lower than the WHO’s recommended reference level of 100 Bq m-3. However, 24% of the surveyed houses exceeded this level, indicating potential health risks. The estimated Potential Alpha Energy Concentration (PAEC) due to its progeny ranged from 1.84 to 18.81 mWL with an average value of 8.24 mWL (SD=3.91). The computed annual effective doses yielded an average value of 3.06 ± 1.44 mSv y1, which is far less than the recommended reference level of 10 mSv y1 by the International Commission on Radiological Protection. The lifetime excess absolute risks varied from 0.4 × 104 to 3.9 × 104, with an average of 1.7 ± 0.8 × 104. Improved the ventilation systems, the application of cements plaster and distempers to the building walls and floor were recommended for older TMHs with ages greater than 50 y to mitigate radon exposure. This data can inform potential policy measures for indoor radon progeny control in Nigeria.
UNSCEAR, “Sources and effects of ionizing radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation UN SCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly, with Scientific Annexes”, New York, NY, 2000. https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/books/9789210582490.
ICRP, “Lung cancer risk from radon and progeny and statement on radon - ICRP publication 115”, Ann ICRP 40 (2010) 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icrp.2011.08.011.
IARC, “IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans; man-made mineral fibres and radon.”, 43 1988. https://books.google.com.ng/books/about/IARC_Monographs_on_the_Evaluation_of_Car.html?id=Kc0K0AEACAAJ&redir_esc=y.
B. Veloso, J. R. Nogueira & M. F. Cardoso, “Lung cancer and indoor radon exposure in the north of Portugal - an ecological study”, Cancer Epidemiol. 36 (2012) 26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2011.10.005.
R. Barbosa-Lorenzo, A. Ruano-Ravina, S. Cerdeira Carames & J. M. ´Barros-Dios, “Residential radon and lung cancer. An ecologic study in Galicia, Spain”, Med. Cl´?nica English Ed. 144 (2015) 304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcle.2015.11.001.
J. Y. Yoon, J. Lee, S. W. Joo & D. R. Kang, “Indoor radon exposure and lung cancer: a review of ecological studies”, Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 28 (2016) 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-016-0098-z.
H. Li, L. Zhang & Q. Guo, “Behaviours and influence factors of radon progeny in three typical dwellings”, J. Radiol. Prot. 31 (2011) 135. https://doi.org/10.1088/0952-4746/31/1/010.
J. Rogado, C. Pangua, G. Serrano-Montero, B. Obispo, A. M. Marino, M. Perez-P ´ erez, A. L ´ opez-Alfonso, P. Gull ´ on & M. ´ A. Lara, “Covid-19 and lung cancer: A greater fatality rate?”, Lung Cancer 146 (2020) 19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.05.034.
S. H. Kim, W. J. Hwang, J. S. Cho & D. R. Kang, “Attributable risk of lung cancer deaths due to indoor radon exposure”, Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 28 (2016) 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-016-0093-4.
WHO, “Who Handbook on Indoor Radon - A Public Health Perspective”, International Journal of Environmental Studies 61 (2009) 100. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207230903556771.
S. Darby, D. Hill, A. Auvinen, J. M. Barros-Dios, H. Baysson, F. Bochicchio, H. Deo, R. Falk, F. Forastiere, M. Hakama, I. Heid, L. Kreienbrock, M. Kreuzer, F. Lagarde, I. Makel ¨ ainen, C. Muirhead, W. Oberaigner, G. ¨Pershagen, A. Ruano-Ravina, E. Ruosteenoja, A. Schaffrath Rosario, M. Tirmarche, L. Toma´sek, E. Whitley, H. E. Wichmann & R. Doll, “Radon ?in homes and risk of lung cancer: collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies”, Br. Med. J. 330 (2005) 223. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.38308.477650.63.
U.S.EPA, “EPA assessment of risks from radon in homes”, Washington, DC, 2003. https://www.epa.gov/radiation/epa-assessment-risks-radon-homes.
N. F. Tawfiq, N. O. Rasheed & A. A. Aziz, “Measurement of indoor radon concentration in various dwellings of Baghdad Iraq”, Int. J. Phys. 3 (2015) 202. https://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/3/5/1/index.html.
O. Y. Morales, T. Martinez, P. Gonzalez, M. Navarrete, L. Cabrera & A. ´Ram´?rez, “Indoor radon levels and gamma-radiation in dwellings of the metropolitan zone of Guadalajara”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 280 (2009) 431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0540-6.
K. Kant, S. B. Upadhyay, G. S. Sharma, and S. K. Chakarvarti, “Radon dosimetry in typical Indian dwellings using plastic track detectors”, Indoor Built Environ. 15 (2006) 187. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X06064091.
M. Minda, G. Toth, I. Horv ´ ath, I. Barnet, K. H ´ amori & E. T ´ oth, “Indoor radon mapping and its relation to geology in Hungary”, Environ. Geol. 57 (2009) 601.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1329-6.
T. Nasir, Matiullah, M. Rafique, S. U. Rahman, M. Khalil & N. Anwar, “Evaluation of radon induced lung cancer risk in occupants of the old and new dwellings of the Dera Ismail Khan City, Pakistan”,
J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 300 (2014) 1209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3095-0.
X. Li, W. Li, H. Shan & F. Wang, “Radon survey in office room and effective dose estimation for staff”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 324 (2020) 561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07082-z.
R. I. Obed, A. K. Ademola & F. O. Ogundare, “Radon measurements by nuclear track detectors in dwellings in Oke-Ogun Area, South-Western, Nigeria”, Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 148 (2012) 475. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncr196.
R. I. Obed, H. T. Lateef & A. K. Ademola, “Indoor radon survey in a university campus of Nigeria.”, J. Med. Phys. 35 (2010) 242. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6203.71760.
O. S. Ajayi, E. O. Owoola, O. E. Olubi & C. G. Dike, “Survey of indoor radon levels in some universities in south western Nigeria”, Radiat. Prot.Dosimetry 187 (2019) 34. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncz134.
R. I. Obed, E. A. Oyelade & H. T. Lateef, “Indoor radon levels in some selected nursery and primary schools in Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria”, J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 11 (2018) 379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2018.07.003.
M. C. Okeji & K. K. Agwu, “Assessment of indoor radon concentration in phosphate fertilizer warehouses in Nigeria”, Radiat. Phys. Chem. 81 (2012) 253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2011.11.052.
O. T. Afolabi, D. T. Esan, B. Banjoko, B. A. Fajewonyomi, J. E. Tobih & B. B. Olubodun, “Radon level in a Nigerian university campus”, BMC Res. Notes 8 (2015) 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-015-1447-7.
O. M. Oni, G. A. Isola, O. O. Oladapo & E. A. Oni, “Estimation of life time fatality risk from indoor radon in some offices in a Nigerian university”, Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 4 (2012) 131. .
O. S. Ajayi & O. E. Olubi, “Investigation of indoor radon levels in some dwellings of southwestern Nigeria”, Environ. Forensics 17 (2016) 275. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2016.1230909.
R. I. Obed, A. K. Ademola, M. Vascotto & G. Giannini, “Radon measurements by nuclear track detectors in secondary schools in oke-ogun region, nigeria”, J. Environ. Radioact. 102 (2011) 1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2011.06.012.
O. Bayode, Y. Michael & D. Adedeji, “Review of economic and environmental bene fi ts of earthen materials for housing in Africa”, Front.Archit. Res. 6 (2017) 519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foar.2017.08.003.
R. L. Njinga, T. L. Ogundele, A. S. Adebayo, M. A. Olatunji, A.
P. Olufemi, C. J. Olowookere, K. Aladeniyi, A. Pereira, M. A. Arogunjo & V. M. Tshivhase, “Distribution dynamics and descriptive statistical analysis of radionuclides in the farmland soils near mining areas in Southwestern Nigeria”, Environ. Geochem. Health 45 (2023) 3617.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01440-4.
A. Mahmood, M. Tufail & M. A. Iqbal, “Measurement of radon con centration and exhalation rate in some mud houses of district Lahore, Pakistan”, Indoor Built Environ. 23 (2014) 774. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X13481235.
J. Salupeto-Dembo, Z. Szabo-Krausz, P. V ´ olgyesi, Z. Kis & C. Szab ¨ o, ´“External radiation exposure of the Angolan population living in adobe houses”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 323 (2020) 353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-019-06920-z.
G. Prasad, G. S. Gusain, V. Joshi & R. C. Ramola, “Assessment of dose due to exposure to indoor radon and thoron progeny”, Nucl. Technol. Radiat. Prot. 25 (2010) 198. https://doi.org/10.2298/NTRP1003198P.
A. E. A. Elzain, “Radon exhalation rates from some building materials used in Sudan”, Indoor Built Environ. 24 (2015) 852. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X14537285.
L. A. Sathish, K. Nagaraja, V. Nagesh & S. Sundareshan, “Survey of indoor concentrations of radon and thoron in homes in Bangalore, India”, Indoor Built Environ. 20 (2011) 278. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X10383477.
N. Nagaiah, L. Sathish, N. Shiva Prasad, M. Ambika, G. Ashok & N. Karunakara, “Residential radon exposure in some areas of Bangalore city, India”, Radiat. Prot. Environ. 35 (2012) 59. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-0464.112338.
S. M. Farid, “Indoor radon in dwellings of Jeddah city, Saudi Ara bia and its correlations with the radium and radon exhalation rates from soil”, Indoor Built Environ. 25 (2016) 269. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X14536749.
J. Salupeto, D. Zsuzsanna, S. Krausz, P. Volgyesi & C. Szab ¨ o, “Radon ´and thoron radiation exposure of the Angolan population living in adobe houses”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 325 (2020) 271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-020-07215-4.
M. Chege, N. Hashim, C. Nyambura, A. Mustapha, M. Hosada & S. Tokonami, “Radon and thoron; Radioactive gases lurking in earthen houses in rural Kenya”, Front. Public Heal. 7 (2019) 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00113.
K. Kant & S. K. Chakarvarti, “Radiological impact of airborne radon and its progeny in dwellings”, Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 42 (2004) 157. https://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/9578.
N. T. A. Nguy ´ ˜en, D. Nguy ˆ˜en-Th ˆ uy, H. Nguy `˜en-V ˆ an, N. Nguy ?˜en-Hai & ˆ
A. Schimmelmann, “Radioactive Thoron 220Rn exhalation from unfired mud building material into room air of Earthen dwellings”, Front. Earth Sci. 9 (2021) 1. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.629241.
R. C. Ramola, M. S. Kandari, R. B. S. Rawat, T. V. Ramachandran & V. M. Choubey, “A study of seasonal variations of radon levels in different types of houses”, J. Environ. Radioact. 39 (1998) 1. https://doi.org/10. 1016/S0265-931X(97)00049-0.
A. M. Maghraby, K. Alzimami & M. Abo-Elmagd, “Estimation of the res idential radon levels and the population annual effective dose in dwellings of Al-kharj, Saudi Arabia”, J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 7 (2014) 577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.09.013.
D. Barooah, S. Barman & S. Phukan, “Simultaneous measurements of radon and thoron & their progeny levels in dwellings on anticlinal structures of Assam, India”, Environ. Monit. Assess. 186 (2014) 3581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3640-x.
M. W. Chege, N. O. Hashim, A. S. Merenga, O. Meisenberg & J. Tschiersch, “Estimation of annual effective dose due to radon and thoron concentrations in mud dwellings of Mrima Hill, Kenya”, Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 167 (2015) 139. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncv231.
M. R. Usikalu, V. Olatinwo, M. Akpochafor, M. A. Aweda, G. Giannini & V. Massimo, “Measurement of Radon concentration in selected houses in Ibadan, Nigeria”, J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 852 (2017) 012028. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/852/1/012028.
V. Duggal, A. Rani & R. Mehra, “Measurement of indoor radon concentration and assessment of doses in different districts of Northern Rajasthan, India”, Indoor Built Environ. 23 (2013) 1142. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X13500801.
R. Sivakumar, “Variability of radon and thoron concentration with type of dwellings in a hilly area”, Indoor Built Environ. 27 (2016) 96. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X16663811.
R. Sivakumar, “Inhalation dose due to radon, thoron & progenies in dwellings of a hill station”, Environ. Monit. Assess. 189 (2017) 96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5767-z.
M. Shakir Khan, A. H. Naqvi & A. Azam, “Study of indoor radon and its progeny levels in rural areas of North India using LR-115 plastic track detectors”, Radiat. Meas. 43 (2008) 385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2008.03.026.
V. Duggal, A. Rani & R. Mehra, “A study of seasonal variations of radon levels in different types of dwellings in Sri Ganganagar district, Rajasthan”, J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 7 (2014) 201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.02.007.
K. Aladeniyi, A. M. Arogunjo, A. J. S. C. Pereira, O. S. Ajayi & I. A. Fuwape, “Radiometric evaluation of indoor radon levels with influence of building characteristics in residential homes from southwestern Nigeria”, Environ. Monit. Assess. 192 (2020) 764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08734-z.
C. A. Oyelami & J. L. Van Rooy, “Geotechnical characterisation of lateritic soils from south-western Nigeria as materials for cost-effective and energy-efficient building bricks”, Environ. Earth Sci. 75 (2016) 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6274-1.
O. S. Ajayi, “Measurement of activity concentrations of 40K, 226Ra and 232Th for assessment of radiation hazards from soils of the southwestern region of Nigeria”, Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 48 (2009) 323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-009-0225-0.
ISO 11665-4 (International Organization for Standardization), “Measure ment of radioactivity in the environment – Air: radon-222 – Part 4: Integrated measurement method for determining average activity concentration using passive sampling and delayed analysis”, Geneva, 2012. https://www.iso.org/standard/52190.html.
K. S. Babai, S. Poongothai, K. S. Lakshmi, J. Punniyakotti & V. Meenakshisundaram, “Estimation of indoor radon levels and absorbed dose rates in air for Chennai city, Tamilnadu, India”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 293 (2012) 649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-012-1718-x.
C. M. Lee, M. H. Kwon, D. R. Kang, T. H. Park, S. H. Park & J. E. Kwak, “Distribution of radon concentrations in child-care facilities in South Korea”, J. Environ. Radioact. 167 (2017) 80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.11.021.
T. H. Park, D. R. Kang, S. H. Park, D. K. Yoon & C. M. Lee, “Indoor radon concentration in Korea residential environments”, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25 (2018) 12678.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1531-3.
N. Ali, W. Muhammad, N. U. Khattak, E. U. Khan, M. U. Rajput, M. Akram, S. Hussain & S. A. Mujahid, “Radon doses in the indoor environments of Murree and Islamabad, Pakistan: A comparison of active and passive techniques”, Indoor Built Environ. 25 (2015) 883. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X15588567.
J. Miles, “Mapping radon-prone areas by lognormal modeling of house radon data”, Health Phys. 74 (1998) 370. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-199803000-00010.
G. W. Lee, J. Y. Yang, H. J. Kim, M. H. Kwon, W. S. Lee, G. H. Kim, D. C. Shin & Y. W. Lim, “Estimation of health risk and effective dose based on measured radon levels in Korean homes and a qualitative assessment for residents’ radon awareness”, Indoor Built Environ. 26 (2017) 1123. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X16664387.
A. Louro, L. Peralta, S. Soares, A. Pereira, G. Cunha, A. Belchior, A. Louro, M. Gil, H. Louro, P. Pinto, M. Joa & P. Teles, “Human exposure to indoor radon : a survey in the region of Guarda , Portugal”, Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 154 (2012) 237. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncs166.
C. K. Kim, S. C. Lee, D. M. Lee, B. U. Chang, B. H. Rho & H. D. Kang, “Nationwide survey of radon levels in Korea”, Health Phys. 84 (2003) 354. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004032-200303000-00008.
R. Sivakumar, “Variability of radon and thoron concentration with type of dwellings in a hilly area”, Indoor Built Environ. 27 (2016) 96. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X16663811.
V. Duggal, R. Mehra & A. Rani, “An investigation of factors influencing indoor radon concentrations in dwellings of Northern Rajasthan, India”, J. Geol. Soc. India 86 (2015) 173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0296-2.
A. Popit & J. Vaupotic, “Indoor radon concentrations in relation to geology in Slovenia”, Environ. Geol. 42 (2002) 330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0526-y.
R. C. Ramola, M. S. Kandari & R. B. S. Rawat, “Assessment of health risk due to exposure of radon and its daughter products in the lower atmosphere”, Curr. Sci. 73 (1997) 771. https://www.jstor.org/stable/24100423.
I. Yarmoshenko, A. Vasilyev, G. Malinovsky, P. Bossew, Z. S. Zuni ? c, A. ´Onischenko & M. Zhukovsky, “Variance of indoor radon concentration: major influencing factors”, Sci. Total Environ. 541 (2016) 155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.077.
R. D. Evans, J. H. Harley, W. Jacobi, A. S. McLean, W. A. Mills & C. J. Stewart, “Estimate of risks from environmental exposure to Radon-222 and its decay products”, Nature 290 (1981) 98. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7207604/.
M. Degerlier & N. Celebi, “Indoor radon concentrations in Adana, Turkey”, Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 131 (2008) 259. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncn157.
M. Rafique, S. Qayyum, S. U. Rahman & Matiullah, “The influence of geology on indoor radon concentrations in neelum valley Azad Kashmir, Pakistan”, Indoor Built Environ. 21 (2012) 718. https://doi.org/10.1177/1420326X11434181.
H. H. Mansour, S. per Khdar, H. Y. Abdulla, N. Q. Muhamad, M. M. Othman & S. Qader, “Measurement of indoor radon levels in Erbil capital by using solid state nuclear track detectors”, Radiat. Meas. 40 (2005) 544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radmeas.2005.06.033.
M. Kumar, A. Agrawal & R. Kumar, “Radiation dose due to radon, thoron and their decay products in indoor environment of Khurja City, U.P., India”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 300 (2014) 39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-2946-z.
K. Alzimami, A. M. Maghraby & M. Abo-Elmagd, “Radon levels and the expected population mortality in dwellings of Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia”, J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 7 (2014) 572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2014.09.009.
B. Kunovska, K. Ivanova, V. Badulin, M. Cenova & A. Angelova, “Assessment of residential radon exposure in Bulgaria”, Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 181 (2018) 34. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncy098.
M. M. Al Bosta, J. J. Al Radaideh & A. M. Ismail, “Indoor 222Rn concentrations and the corresponding lung cancer risk in Celein region, west of Al Khums, Libya”, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 285 (2010) 641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-010-0597-2.
Z. Stojanovska, J. Januseski, B. Boev & M. Ristova, “Indoor exposure of population to radon in the FYR of Macedonia”, Radiat. Prot. Dosimetry 148 (2012) 162. https://doi.org/10.1093/rpd/ncr030.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Kehinde Aladeniyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






