Ensemble machine learning algorithm for cost-effective and timely detection of diabetes in Maiduguri, Borno State
Keywords:
Ensemble learning, Diabetes, Weighted average ensemble, Random forests, Light gradient boosting machineAbstract
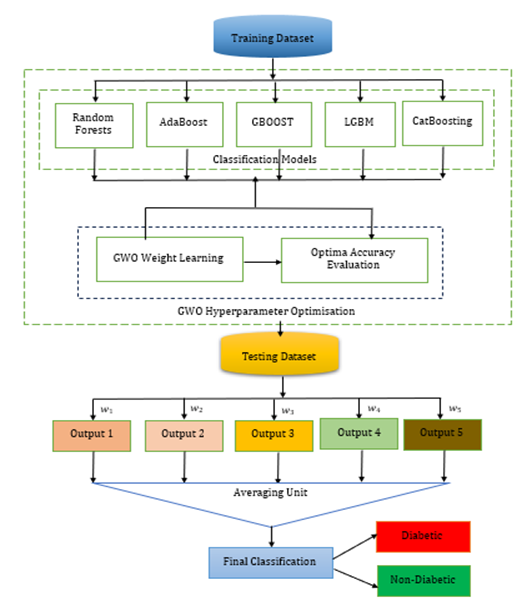
Diabetes is a serious medical condition that severely hinders the body's ability to produce or properly regulate insulin, leading to detrimental carbohydrate metabolism and dangerously high blood sugar levels. This ultimately causes inadequate carbohydrate metabolism and heightened blood glucose levels. Alarmingly, from 2000 to 2019, diabetes-related mortality rates rose by 3%. In the year 2019 alone, diabetes was tragically responsible for nearly 2 million deaths. This groundbreaking research introduces the improved weighted average ensemble learning (WAEL) model as an innovative solution for detecting diabetes. The enhanced WAEL model effectively addresses the overfitting challenge by integrating multiple models that have gained unique insights from the data. The proposed WAEL model ingeniously combines five feature spaces through the grey wolf optimisation (GWO) algorithm to uncover the optimal weight combination. GWO plays a vital role in weight optimization, enabling the reduction of weights in models that are particularly sensitive to noise. The results demonstrated that the improved WAEL achieved an astounding level of accuracy, soaring to 98.90%. The LGBM algorithm followed closely, achieving an impressive accuracy of 85.00%. The RF method recorded an accuracy of 81.00%. When it comes to accurately identifying diabetes, the improved WAEL ensemble model significantly outperformed the other five individual models, as evidenced by metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. Therefore, the proposed model stands as a compelling alternative tool for healthcare professionals in the early detection of diabetes.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Emmanuel Gbenga Dada, Aishatu Ibrahim Birma, Abdulkarim Abbas Gora

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- David Opeoluwa Oyewola, Emmanuel Gbenga Dada, Juliana Ngozi ndunagu, Terrang Abubakar Umar, Akinwunmi S.A, COVID-19 Risk Factors, Economic Factors, and Epidemiological Factors nexus on Economic Impact: Machine Learning and Structural Equation Modelling Approaches , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021







