Preliminary Investigation of Microplastic as a Vector for Heavy Metals in Bye-ma Salt Mine, Wukari, Nigeria
Keywords:
microplastics, sediment, aquatic, heavy metals, functional groupAbstract
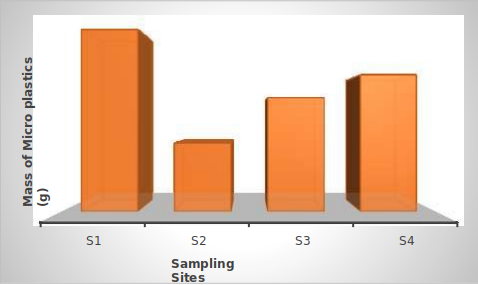
This study is aimed at the preliminary investigation of microplastics as carrier of heavy metals pollution in surface sediment. Heavy metals concentration was determined by FAAS while microplastics characterization was analysed by ATR-FTIR spectrophotometer. The results obtained showed high level of lead (Pb) concentrations which ranged from 21.37 - 32.80 mg/kg across the sampling sites while Cd has the least concentration between 0.04 - 0.80 mg/kg. The concentration of Pb and Cd were above the USEPA permissible limit in sediment. The following absorption bands; 2978.19, 1728.28 and 1458.23 cm-1 with the functional groups; C-H stretch, C=O stretch and CH2 bend indicates the presence of Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) in site S2 and S4 respectively. Other microplastics found in the sampling sites are Nylon, Nitrile, Polycarbonate and Poly propylene. This indicates that there is identical distribution of the microplastics in the sampling sites. The quantities of microplastics isolated ranged from 8.11 - 8.16 g across the sites. Aquatic organisms fed on these polymeric materials because of their unique appearance. Hence, heavy metals adsorption will lead to higher concentrations on microplastics which could be ingested and lead serious complication in their intestine.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Godwin O. Olutona, Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment of Tropical Freshwater Stream , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- M. A. Lala, S. Kawu, O. A. Adesina, J. A. Sonibare, Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution Status in Surface Soil of a Nigerian University , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- E. P. Onokare, L. O. Odokuma, F. D. Sikoki, B. M. Nziwu, P. O. Iniaghe, J. C. Ossai, Physicochemical Characteristics and Toxicity Studies of Crude Oil, Dispersant and Crude Oil-Dispersant Test Media to Marine Organisms , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- J. A. Akinpelu, K. P. Ojo, S. O. Salawu, G. O. Olutona, F. O. Aweda, O. O. Jegede, Concentrations of heavy metal content in indoor dust and potential exposure in preschool children , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 8, Issue 1, February 2026 (In Progress)
- E. O. Echeweozo, C. I. Nworie, A. O. Ojobeagu, P. B. Otah, I. J. Okoro, Health risk assessment due to environmental radioactivity and heavy metal contamination at the central solid waste dumpsite in Ebonyi State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- D. D. Bwede, R. A. Wuana, G. O. Egah, A. U. Itodo, E. Ogah, E. A. Yerima, A. I. Ibrahim, Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- S. A. Yamusa, A. Shaari, I. Isah, U. B. Ibrahim, S. I. Kunya, S. Abdulkarim, Y. S. Itas, M. Alsalamh, Effects of Exchange Correlation Functional (Vwdf3) on the Structural, Elastic, and Electronic Properties of Transition Metal Dichalogenides , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- K. O. Sodeinde, S. O. Olusanya, D. U. Momodu, V. F. Enogheghase, O. S. Lawal, Waste glass: An excellent adsorbent for crystal violet dye, Pb2+ and Cd2+ heavy metals ions decontamination from wastewater , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- D. N. Ajah, E. Agboeze, J. N. Ihedioha, E. Chukwudi-Madu, C. C. Chime, Levels of Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), and Cadmium (Cd) in Soil, Rice Stalk, and Oryza Sativa Grain in Ishiagu Rice Field, Ebonyi State, Nigeria; Human Health Risk , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Suha Ibrahim Salih Al-Ali, Zaidun Naji Abudi, Mohammed Nsaif Abbas, Modelling and Simulation for the use of Natural Waste to Purified Contaminated Heavy Metals , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






