Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel XC70 in 1M HCl solution using Balanite Aegyptiaca extracts as an eco-friendly inhibitor
Abstract
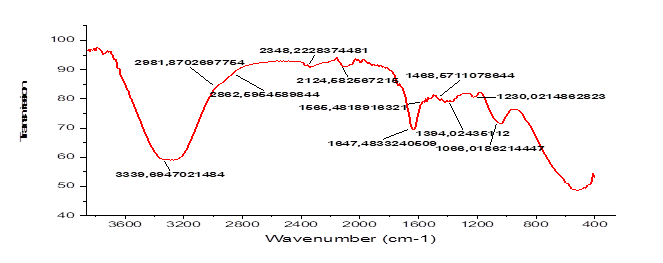
The corrosion inhibition effect of Balanites aegyptiaca leaves extracts on carbon steel XC70 in 1 M hydrochloric acid solution has been studied using gravimetric study and Potentiodynamic polarization method. The plant extracts has proven its ability to stabilize metal corrosion, as FTIR curves confirm that extracts has compounds rich in oxygen atom and aromatic compounds. The results show that the inhibition efficiency increases with increase in extract concentration and decreases with rise in temperature. The inhibition efficiency from weight loss studies was found to be more than 90 % at 50 % volumic concentration while this inhibition efficiency was obtained from Potentiodynamic polarization studies at 150 ppm. We also investigated the effect of temperature on corrosion with and without the optimal concentration in the temperature range of 293 to 373 K and calculated the activation energy, enthalpy, and entropy. The thermodynamic results showed that the plant extract particle’s adsorption process on the steel’s surface was endothermic and physical in nature. Tafel curve analysis revealed that our green inhibitor worked as a mixed-type inhibitor, bottled up the corrosion processes of steel X70 in hydrochloric acid, and their adsorption was found to follow the Langmuir and Temkin models.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 nedjimi mohammed said, Yazid amri, belalem Mohammed Abdelkader, Guerguer Louiza, tlili salah (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






