Zinc oxide nanoparticles and nanorods: advanced sunscreen ingredients for enhanced UV protection and radiation filtration
Authors
-
Ammar A. Oglat
Department of Medical Imaging, Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, 13133, Jordan
-
Abdallah Al Said
School of Physics, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800 USM Penang, Malaysia
-
Naser M. Ahmed
Laser and Optoelectronics Engineering Department, Dijlah University College, Baghdad, Iraq
-
Mohammed Dawood Salman
Department of Medical Physics, College of Applied Sciences, University of Fallujah, Iraq
Keywords:
Zinc oxide, UV absorption, Nanoparticles, Sunscreen, Sun protection factor (SPF), Critical wavelengthAbstract
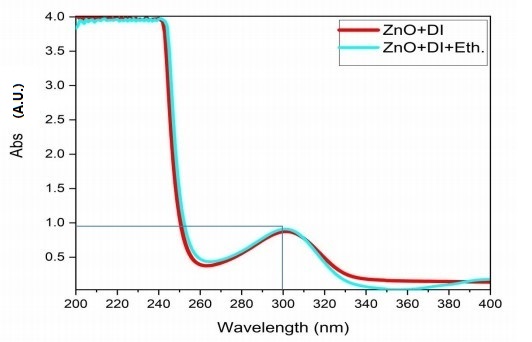
Due to its high ability to absorb ultraviolet rays in a wide spectrum, zinc oxide has emerged as the most important element used in the manufacture of sunscreens and cosmetics. This study aimed to determine the composition of zinc oxide nanorods and nanoparticles, as well as their impact on UV ray absorption. This was done by using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM-EDS) and Ultra Violet (UV-Visible) spectroscopy to look at sunscreen samples that had different amounts of zinc oxide added to them. We prepared two types of commercial zinc oxide powder using a chemical bath deposition method. After characterizing samples of the two powders using FESEM-EDS spectroscopy, various shapes emerged, with rods dominating in both powders. The length of the structure was 224.7 nm, 9.443 ?m, and the diameter was 75.65 nm, 859.9 nm, respectively. The sun protection factor and the critical wavelength for the prepared samples were calculated using UV-Visible spectroscopy to measure the absorbance. An increasing zinc oxide to a certain extent led to an increase in UV ray absorption in all regions of the UV ray wavelength, with the ideal zinc oxide ratio being. The sunscreen had a concentration of 27.5%, and the use of zinc oxide provided broad protection from ultraviolet rays in all samples at the critical wavelength. In conclusion, increasing zinc oxide concentration in sunscreen increased the sun protection factor, critical wavelength, and UV ray protection.
[1] B. Bhushan, Introduction to nanotechnology, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2017, pp. 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54357-3_1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54357-3_1
[2] E. Y. Salih, A. Ramizy, O. Aldaghri, M. H. Eisa & K. H. J. M. L. Ibnaouf, “Solution processed self-powered broadband flower-like Zn (Al) O-mixed metal oxide dye sensitized photodetector”, Materials Letters 362 (2024) 136213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2024.136213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2024.136213
[3] A. H. Rajpar, M. B. A. Bashir, E. Y. Salih & E. M. J. N. Ahmed, “Fabrication and enhanced performance evaluation of TiO2@ Zn/Al-LDH for DSSC application: The influence of post-processing temperature”, Nanomaterials 14 (2024) 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110920. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14110920
[4] M. C. Roco, “The long view of nanotechnology development: the National Nanotechnology Initiative at 10 years”, Journal of Nanoparticle Research 13 (2024) 427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0192-z. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-0192-z
[5] M. Ali Dheyab, A. Abdul Aziz, M. S. Jameel, P. Moradi Khaniabadi & A. A. Oglat, “Rapid sonochemically-assisted synthesis of highly stable gold nanoparticles as computed tomography contrast agents”, Applied Sciences 10 (2020) 7020. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207020
[6] W. S. Khan, E. Asmatulu & R. Asmatulu, “Nanotechnology emerging trends, markets and concerns”, in Nanotechnology safety, Elsevier, 2025, pp. 1–21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59438-9.00001-1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-15904-6.00017-4
[7] S. Yeoh, M. Matjafri, K. Mutter & A. A. Oglat, “Plastic fiber evanescent sensor in measurement of turbidity”, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 285 (2019) 1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.10.042. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.10.042
[8] M. Nasrollahzadeh, S. M. Sajadi, M. Sajjadi & Z. Issaabadi, “An introduction to nanotechnology”, in Interface science and technology, Elsevier, 2019, pp. 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813586-0.00001-8.
[9] A. S. ALmomani, A. F. Omar, A. A. Oglat, S. S. Al-Mafarjy, M. A. Dheyab & T. H. J. S. Khazaalah, “Developed a unique technique for creating stable gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) to explore their potential against cancer”, South African Journal of Chemical Engineering 53 (2025) 142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2025.04.012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2025.04.012
[10] S. Mohapatra, S. Ranjan, N. Dasgupta, S. Thomas & R. K. Mishra, “Characterization and Biology of nanomaterials for drug delivery: nanoscience and nanotechnology in drug delivery”, in Nanoscience and nanotechnology in drug delivery, Elsevier, 2018, pp. 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813586-0.00001-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-813586-0.00001-8
[11] E. Y. Salih, M. F. M. Sabri, M. Z. Hussein, K. Sulaiman, S. M. Said, B. Saifullah & M. B. Bashir, “Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO/ZnAl 2 O 4 nanocomposites prepared via thermal reduction approach”, Journal of Materials Science 53 (2018) 581. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10853-017-1504-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1504-9
[12] N. Prajitha, S. Athira & P. J. Mohanan, “Bio-interactions and risks of engineered nanoparticles”, Environmental Research 172 (2019) 98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.02.003
[13] Q. Abbas, B. Yousaf, M. U. Ali, M. A. Munir, A. El-Naggar, J. Rinklebe & M. J. E. i. Naushad, “Transformation pathways and fate of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) in distinct interactive environmental compartments: A review”, Environment International 138 (2020) 105646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105646. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105646
[14] M. A. Dheyab, P. M. Khaniabadi, A. A. Aziz, M. S. Jameel, B. Mehrdel, A. A. Oglat & H. A. J. P. Khaleel, “Focused role of nanoparticles against COVID-19: Diagnosis and treatment”, Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy 34 (2021) 102287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102287. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102287
[15] O. F. Farhat, M. Husham, M. Bououdina, A. Abuelsamen, A. A. Oglat & N. J. Mohammed, “Tape-based novel ZnO nanoaggregates photodetector”, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical 332 (2021) 113210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.113210. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.113210
[16] M. A. Bhat, K. Gedik & E. O. Gaga, “Environmental impacts of nanoparticles: pros, cons, and future prospects”, in Synthesis of bionanomaterials for biomedical applications, Elsevier, 2023, pp. 493–528. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91195-5.00002-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-91195-5.00002-7
[17] E. Y. Salih, Z. Abbas, S. H. H. Al Ali & M. Z. J. A. i. M. S. Hussein, “Dielectric behaviour of Zn/Al?NO3 LDHs filled with polyvinyl chloride composite at low microwave frequencies”, Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 1 (2014) 647120. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/647120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/647120
[18] B. Bocca, B. Battistini, V. Leso, L. Fontana, S. Caimi, M. Fedele & I. J. T. Iavicoli, “Occupational exposure to metal engineered nanoparticles: a human biomonitoring pilot study involving Italian nanomaterial workers”, Toxics 11 (2023) 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020120
[19] G. Singh, N. Thakur & R. J. Kumar, “Nanoparticles in drinking water: Assessing health risks and regulatory challenges”, Science of The Total Environment 1 (2024) 174940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174940. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174940
[20] C. Domingues, A. Santos, C. Alvarez-Lorenzo, A. Concheiro, I. Jarak, F. Veiga, I. Barbosa, M. Dourado & A. J. A. n. Figueiras, “Where is nano today and where is it headed? a review of nanomedicine and the dilemma of nanotoxicology”, ACS Nano 16 (2022) 9994. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c00128. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c00128
[21] A. Mohajerani, L. Burnett, J. V. Smith, H. Kurmus, J. Milas, A. Arulrajah, S. Horpibulsuk & A. J. M. Abdul Kadir, “Nanoparticles in construction materials and other applications, and implications of nanoparticle use”, Materials 12 (2019) 3052. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193052. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12193052
[22] E. Bergamaschi, I. G. Canu, A. Prina-Mello & A. Magrini, “Biomonitoring”, in Adverse effects of engineered nanomaterials, Academic Press, 2017, pp. 125–158. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809199-9.00006-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809199-9.00006-9
[23] A. M. Lopes, H. U. Dahms, A. Converti & G. L. Mariottini, “Role of model organisms and nanocompounds in human health risk assessment”, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 193 (2021) 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09066-2. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09066-2
[24] D. Romeo, R. Hischier, B. Nowack, O. Jolliet, P. Fantke & P. J. Wick, “In vitro-based human toxicity effect factors: challenges and opportunities for nanomaterial impact assessment”, Environmental Science: Nano 9 (2022) 1913. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01014J. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN01014J
[25] D. R. Hristozov, S. Gottardo, A. Critto & A. J. N. Marcomini, “Risk assessment of engineered nanomaterials: a review of available data and approaches from a regulatory perspective”, Nanotoxicology 6 (2012) 880. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.626534. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.626534
[26] B. Annangi, L. Rubio, M. Alaraby, J. Bach, R. Marcos & A. J. Hernández, “Acute and long-term in vitro effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles”, Archives of Toxicology 90 (2016) 2201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1613-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1613-7
[27] V. De Matteis, “Exposure to inorganic nanoparticles: routes of entry, immune response, biodistribution and in vitro/in vivo toxicity evaluation”, Toxics 5 (2017) 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5040029. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics5040029
[28] A. Juzeniene & J. Moan, “Beneficial effects of UV radiation other than via vitamin D production”, Dermato-Endocrinology 4 (2012) 109. https://doi.org/10.4161/derm.20013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4161/derm.20013
[29] B. Wadhwa, V. Relhan, K. Goel, A. M. Kochhar & V. K. Garg, “Vitamin D and skin diseases: a review”, Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology 81 (2015) 344. https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.159929. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.159928
[30] H. Soehnge, A. Ouhtit & O. Ananthaswamy, “Mechanisms of induction of skin cancer by UV radiation”, Frontiers in Bioscience 2 (1997) 538. https://doi.org/10.2741/a211. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2741/A211
[31] B. Kozma & M. J. Eide, “Photocarcinogenesis: an epidemiologic perspective on ultraviolet light and skin cancer”, Dermatologic Clinics 32 (2014) 301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2014.03.004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.det.2014.03.004
[32] N. Hasan, A. Nadaf, M. Imran, U. Jiba, A. Sheikh, W. H. Almalki, S. S. Almujri, Y. H. Mohammed, P. Kesharwani & F. J. Ahmad, “Skin cancer: understanding the journey of transformation from conventional to advanced treatment approaches”, Molecular Cancer 22 (2023) 168. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01854-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-023-01854-3
[33] Y. Shi, J. Du & J. J. Qiu, “A novel double 3D continuous phase composite with ultra-broadband wave absorption from gigahertz to UV–vis-NIR for extremely cold environment”, Chemical Engineering Journal 436 (2022) 135220. https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3994402. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135220
[34] J. Li, N. Arif, T. Lv, H. Fang, X. Hu & Y. Zeng, “Towards full?spectrum photocatalysis: Extending to the near?infrared region”, ChemCatChem 14 (2022) e202200361. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202200361. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202200361
[35] S. B. Saha, A. Saha, P. Das, A. Kakati, A. Banerjee & P. Chattopadhyay, “A comprehensive review of ultraviolet radiation and functionally modified textile fabric with special emphasis on UV protection”, Heliyon 10 (2024) e40027. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40027. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40027
[36] A. Svobodova, D. Walterova & J. Vostalova, “Ultraviolet light induced alteration to the skin”, Biomedical Papers-Palacky University in Olomouc 150 (2006) 25. https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2006.003. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5507/bp.2006.003
[37] M. D. Salman, Y. M. Radzi, E. Y. Salih, A. A. Oglat, A. A. Rahman & M. A. Dheyab, “Synthesis techniques and modern applications of copper oxide nanoparticles in cancer treatment and radiotherapy: A review”, Journal of Molecular Structure 1322 (2024) 140301. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.140301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.140301
[38] M. D. Salman, Y. M. Radzi, A. A. Oglat, R. W. Kolaib, A. Idris, M. Alhassan, W. A. Alton & A. Rahman, “Enhancing the acoustic properties for a novel radiation dosimetry PMMAG by optimizing the stability of copper oxide nanoparticles”, BioNanoScience 15 (2025) 1. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12668-025-01900-y. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-025-01900-y
[39] M. D. Salman, Y. M. Radzi, A. A. Rahman & A. A. Oglat, “Ultrasound evaluation of polymathic methacrylate (PMMA) gel dosimeter doped with copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles”, Physica Scripta 99 (2024) 085307. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ad623b. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1402-4896/ad623b
[40] A. Abuelsamen, S. Mahmud, G. N. Makhadmeh, T. AlZoubi, A. Al Diabat, N. A. Algadri, O. A. Noqta, E. Absi, A. M. S. A. Majid & A. A. Oglat, “Pluronic F-127-coated ZnO nanoparticles as superior photosensitizers for effective bladder cancer photodynamic therapy: In-vitro evaluation”, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 95 (2024) 105550. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105550. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105550
[41] O. Farhat, M. Halim, N. M. Ahmed, A. A. Oglat, A. Abuelsamen, M. Bououdina & M. J. Qaeed, “A study of the effects of aligned vertically growth time on ZnO nanorods deposited for the first time on Teflon substrate”, Applied Surface Science 426 (2017) 906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.031
[42] U. Bashir, Z. Hassan, N. M. Ahmed, A. Oglat & A. J. Yusof, “Sputtered growth of high mobility InN thin films on different substrates using Cu-ZnO buffer layer”, Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing 71 (2017) 166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.07.025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.07.025
[43] J. K. Robinson, S. Patel, S. Y. Heo, E. Gray, J. Lim, K. Kwon, Z. Christiansen, J. Model, J. Trueb & A. Banks, “Real-time UV measurement with a sun protection system for warning young adults about sunburn: prospective cohort study”, JMIR mHealth and uHealth 9 (2021) e25895. https://doi.org/10.2196/25895. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2196/25895
[44] O. P. Egambaram, S. Kesavan Pillai & S. Ray, “Materials science challenges in skin UV protection: a review”, Photochemistry and Photobiology 96 (2020) 779. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13208. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/php.13208
[45] H. Gulab, N. Fatima, U. Tariq, O. Gohar, M. Irshad, M. Z. Khan, M. Saleem, A. Ghaffar, M. Hussain & A. Jan, “Advancements in zinc oxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, and diverse applications”, Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects 39 (2024) 101271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2024.101271. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2024.101271
[46] A. A. Oglat, “Gamma ray, beta and alpha particles as a sources and detection”, Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 16 (2023) 100503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2022.100503. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2022.100503
[47] A. A. Oglat, “Comparison of X-ray films in term of kVp, mA, exposure time and distance using Radio-graphic Chest Phantom as a radiation quality”, Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 15 (2022) 100479. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2022.100479. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2022.100479
[48] R. Abdalrheem, F. Yam, A. R. Ibrahim, H. Lim, K. Beh, O. F. Farhat, A. A. Oglat & A. Abuelsamen, “Exploring 1-butanol as a potential liquid precursor for graphene synthesis via chemical vapour deposition and enhanced catalyzed growth methodology”, Journal of Nanoparticle Research 21 (2019) 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4650-y. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-019-4650-y
[49] O. F. Farhat, M. Hisham, M. Bououdina, A. A. Oglat & N. Mohammed, “Growth of ZnO nanostructures by wet oxidation of Zn thin film deposited on heat-resistant flexible substrates at low temperature”, Semiconductors 54 (2020) 1220. http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620100103. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782620100103
[50] O. V. Yakubovich, G. V. Kiriukhina, A. S. Volkov & O. V. Dimitrova, “A rare case of Na/Zn isomorphism in the crystal structure of acentric zincophosphate Na5Zn [Zn (PO4) 3]”, Structural Science 81 (2025) 62. https://doi.org/10.1107/s2052520624011156. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052520624011156
[51] X. Zhao, C. Yang & M. J. Chen, “Aqueous multivalent metal ion batteries: Fundamental mechanism and applications”, in Towards next generation energy storage technologies: From fundamentals to commercial applications, 2024, pp. 249–287. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/9783527845316.ch7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527845316.ch7
[52] M. Alshipli, T. A. Altaim, M. Aladailah, A. A. Oglat, S. A. Alsenany, O. Tashlykov, S. M. F. Abdelaliem, M. Marashdeh, R. Banat & D. J. Pyltsova, “High-density polyethylene with ZnO and TiO2 nanoparticle filler: Computational and experimental studies of radiation-protective characteristics of polymers”, Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 16 (2023) 100720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2023.100720. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrras.2023.100720
[53] R. Abdalrheem, F. Yam, A. R. Ibrahim, H. Lim, K. Beh, A. A. Ahmed, A. A. Oglat, K. M. Chahrour, O. F. Farhat & N. J. Afzal, “Improvement in photodetection characteristics of graphene/p-Silicon heterojunction photodetector by PMMA/graphene cladding layer”, Journal of Electronic Materials 48 (2019) 4064. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07170-1. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07170-1
[54] R. Abdalrheem, F. Yam, A. R. Ibrahim, K. Beh, Y. Ng, F. Suhaimi, H. Lim, M. M. Jafri & A. A. Oglat, “Comparative studies on the transfer of chemical vapor deposition grown graphene using either electrochemical delamination or chemical etching method”, in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing, 2018, p. 012038. http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1083/1/012038. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1083/1/012038
[55] E. A. Dutra, D. A. Oliveira, E. Kedor-Hackmann & M. I. Santoro, “Determination of sun protection factor (SPF) of sunscreens by ultraviolet spectrophotometry”, Revista Brasileira de Ciências Farmacêuticas 40 (2004) 381. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1516-93322004000300014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-93322004000300014
[56] E. Elahi, M. F. Khan, S. Rehman, H. W. Khalil, M. A. Rehman, D. Kim, H. Kim, K. Khan, M. Shahzad & M. W. Iqbal, “Enhanced electrical and broad spectral (UV-Vis-NIR) photodetection in a Gr/ReSe 2/Gr heterojunction”, Dalton Transactions 49 (2020) 10017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/D0DT01164A. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0DT01164A
[57] N. S. Bora, M. P. Pathak, S. Mandal, B. Mazumder, R. Policegoudra, P. S. Raju & P. Chattopadhyay, “Safety assessment and toxicological profiling of a novel combinational sunprotective dermal formulation containing melatonin and pumpkin seed oil”, Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 89 (2017) 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.07.004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.07.004
[58] A. Ali, A.-R. Phull & M. Zia, “Elemental zinc to zinc nanoparticles: Is ZnO NPs crucial for life? Synthesis, toxicological, and environmental concerns”, Nanotechnology Reviews 7 (2018) 413. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0067. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/ntrev-2018-0067
[59] T. H. Kim, S. H. Park, S. Lee, A. S. Bharadwaj, Y. S. Lee, C. G. Yoo & T. H. Kim, “A review of biomass-derived UV-shielding materials for bio-composites”, Energies 16 (2023) 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052231. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052231
[60] A. A. Oglat, S. M. Shalbi & M. Suhimi, “Adding barium sulfate (BaSO4) to fly ash geopolymer increases its compressive strength as X-ray shielding for medical imaging applications”, Cleaner Waste Systems 9 (2024) 100175. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clwas.2024.100175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clwas.2024.100175
[61] M. Alshipli, M. Aladailah, M. Marashdeh, A. A. Oglat, H. Akhdar, O. Tashlykov, R. Banat & A. T. Walaa, “Fe-nanoparticle effect on polypropylene for effective radiation protection: Simulation and theoretical study”, Medical Engineering & Physics 121 (2023) 104066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2023.104066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2023.104066
[62] E. T. Salim, M. A. Fakhri, S. M. Tariq, A. S. Azzahrani, R. K. Ibrahim, A. A. Alwahib, S. F. H. Alhasan, A. Ramizy, E. Y. Salih & Z. T. Salim, “The unclad single-mode fiber-optic sensor simulation for localized surface plasmon resonance sensing based on silver nanoparticles embedded coating”, Plasmonics 19 (2024) 131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01949-z. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01949-z
[63] M. K. Mohammed, A. M. Naji, D. S. Ahmed, M. J. Jamai, E. Y. Salih, M. Dehghanipour, S. Bhattarai, R. Pandey, J. Madan & M. F. Rahman, “Facile synthesis of chitosan-MoS2 over reduced graphene oxide to improve photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue”, Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 1 (2024) 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-024-06619-y. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-024-06619-y
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Ammar A. Oglat, Abdallah Al Said, Naser M. Ahmed, Mohammed Dawood Salman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







