Fabrication and Characterization of a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell using Natural Dye Extract of Rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as Photosensitizer
Keywords:
natural dyes, energy conversion efficiency, photosensitizers, absorption spectra, anchorage, dye-sensitized solar cellsAbstract
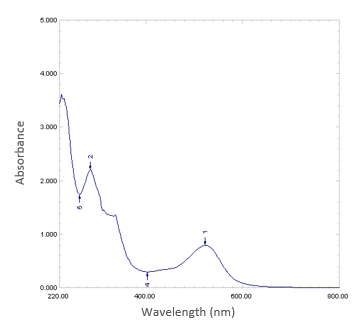
The relatively low energy conversion efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) is a key challenge hindering the commercialization of the solar cell. The photochemical performance of the dye used as a photosensitizer for the DSSC greatly determines the efficiency of the solar cell. This study demonstrates the suitability of dye extracted from rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) flowers as a photosensitizer for a DSSC. The natural dye was extracted using the acid water extraction method and was characterized using FTIR spectroscopy and UV–vis spectrophotometry. The absorption spectra of the dye were examined to determine the aptness of the dye as a photosensitizer in DSSCs. The IR absorption spectra of the extracted dye confirmed both amine and hydroxyl compounds as functional groups in the natural dye, which established the suitability of the dye as a photosensitizer in DSSCs.The UV-vis absorption spectra of the natural dye within the visible region illustrate that the aqueous extract from rosella flowers has stable absorption of visible light, thus validating the natural dye as a good candidate for photosensitizer in a DSSC. The fabricated DSSC delivered a short-circuit current of 5 ?A and an open-circuit voltage of 0.637 V.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- A. A. Willoughby, M. E. Sanyaolu, M. O. Osinowo, A. O. Soge, O. F. Dairo, Estimation of some Radio Propagation Parameters using Measurements of Surface Meteorological Variables in Ede, Southwest Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023






