Forecasting of the epidemiological situation: Case of COVID-19 in Morocco
Keywords:
ARIMA, COVID-19, Pandemic, FBProphet, Time series forecastingAbstract
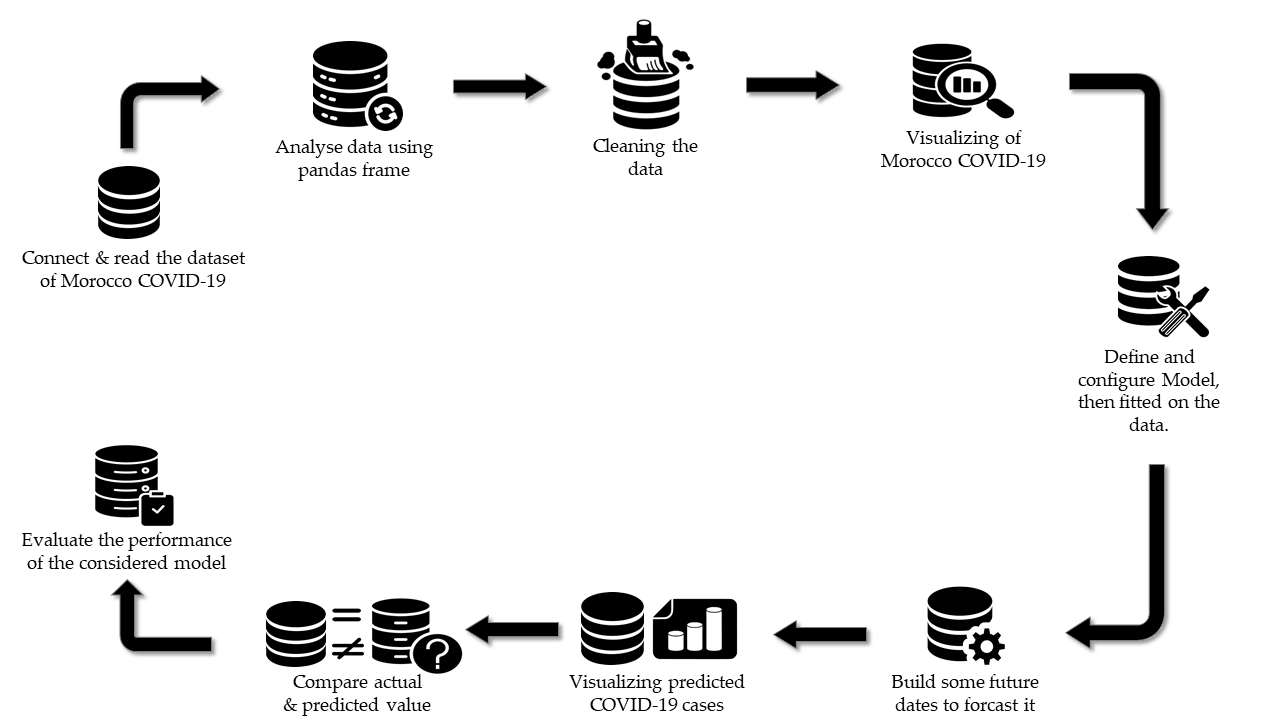
Since the coronavirus pandemic started, many people have died due to the disease. The epidemic has been challenging to predict, as it progresses and spreads throughout the world. We used Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models to predict the outbreak of COVID-19 in the upcoming months in Morocco. In this work, we measured the effective reproduction number using the real data and the forecasted data produced by the two commonly used approaches, to reveal how effective the measures taken by the Moroccan government have been in controlling the COVID-19 outbreak. The prediction results for the next few months show a strong evolution in the number of confirmed and death cases in Morocco. We study the spread of COVID-19 in Morocco to see how many cases are discovered, recovered, and dead, and the forecasting of further cases is used as a basic novel method. It is based on time series models. We used coronavirus outbreak data from March 02, 2020, to August 04, 2021. ARIMA (Autoregressive integrated moving average) and Prophet time-series models are used to forecast the development of COVID-19, which is not a novel method. The mean absolute error, root mean square error, and coefficient of determination R2 were computed to assess the model's performance. Our study aims to provide a better understanding of the infectious disease outbreak that affected Morocco. It also provides information on the disease outbreak's epidemiology. Our study shows that the FBProphet model is more accurate in predicting the prevalence of COVID-19. It can help guide the government's efforts to prevent the virus' spread.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 El Mehdi Chouit, Mohamed RACHDI, Mostapha BELLAFKIH, Brahim RAOUYANE

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- F. O. Aweda, J. A. Akinpelu, T. K. Samson, M. Sanni, B. S. Olatinwo, Modeling and Forecasting Selected Meteorological Parameters for the Environmental Awareness in Sub-Sahel West Africa Stations , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- Gabriel O. Odekina, Adedayo F. Adedotun, Ogbu F. Imaga, Modeling and Forecasting the Third wave of Covid-19 Incidence Rate in Nigeria Using Vector Autoregressive Model Approach , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- Akeem Olarewaju Yunus, Morufu Oyedunsi Olayiwola, The analysis of a novel COVID-19 model with the fractional-order incorporating the impact of the vaccination campaign in Nigeria via the Laplace-Adomian Decomposition Method , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- A. F. Adedotun, T. Latunde, O. A. Odusanya, Modelling and Forecasting Climate Time Series with State-Space Model , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 2, Issue 3, August 2020
- Samuel Olorunfemi Adams, Davies Abiodun Obaromi, Alumbugu Auta Irinews, Goodness of Fit Test of an Autocorrelated Time Series Cubic Smoothing Spline Model , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- Umaru Hassan, Mohd Tahir Ismail, Improving forecasting accuracy using quantile regression neural network combined with unrestricted mixed data sampling , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- Joel Ndam, O. Adedire, Comparison of the Solution of the Van der Pol Equation Using the Modified Adomian Decomposition Method and Truncated Taylor Series Method , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 2, Issue 2, May 2020
- E. A. Nwaibeh, M. K. M. Ali, M. O. Adewole, The dynamics of hybrid-immune and immunodeficient susceptible individuals and the three stages of COVID-19 vaccination , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- Gabriel James, Ime Umoren, Anietie Ekong, Saviour Inyang, Oscar Aloysius, Analysis of support vector machine and random forest models for classification of the impact of technostress in covid and post-covid era , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- Elsayed Elshoubary, Effect of reduction method on the performance a software defined network system using Gumbel Hougaard family copula distribution , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






