Characterizations of Galena as Potential Photosensitizer in a Natural Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell
Keywords:
Galena, Mineral, Dyes, PhotosensitizersAbstract
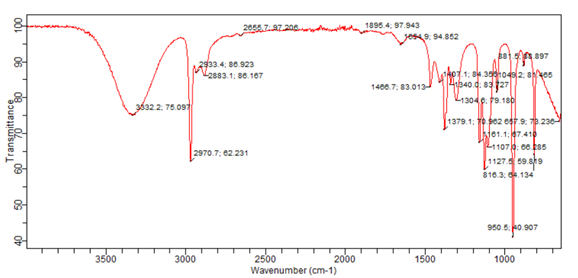
Dye is one of the principal parts for high power conversion efficiency in a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Conspicuous developments have taken place via the work of several researchers in the engineering of novel dye structures so as to enhance the performance of the system. The properties of a natural mineral dye were studied in this work. The structure of the dye was determined and discovered to have contains constituents that could enhance better absorption of solar radiation for use in a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell (DSSC). The Lead sulphide and iron content of the mineral dye studied as revealed by the X-Ray diffraction analysis done suggest this. The X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) done revealed that the concentration of Lead and Iron (Fe) is high as compared to other elements present in the material, probably as a result of the fact that it is a geological sample (of the earth) and which may even suggest its colour and hence makes it absorbs solar radiation of visible region at its wavelength (around 380 nm – 800 nm). The functional groups present in the dye as obtained from the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy are the Amine, Carbonyl, and hydroxyl groups, all of which confirm the suitability of the dye material in photosensitizing a semiconductor in a DSSC. The absorption spectra of the dye within the visible region of electromagnetic radiation show that the material has high, increased, and stable absorption of visible light which is suggesting a more durable natural dye for a DSSC than the easily degraded natural dyes of plants source.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- A. A. Willoughby, A. A. Soge, O. F. Dairo, O. D. Olukanni, E. U. Durugbo, W. S. Michael, T. A. Adebayo, Fabrication and Characterization of a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell using Natural Dye Extract of Rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as Photosensitizer , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- Afizu Mamudu, Eti-mbuk S. Akanbi, Shola C. Odewumi, Hydrothermal alteration and mineral potential zones of Bauchi area Northeastern Nigeria using interpretation of aeroradiometric data , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 1, February 2025
- S. A. Adepoju, O. J. Ojo, O. Olaniyan, T. E. Bamidele, I. S. Usman, Sedimentological and weathering signature investigation of claystones from Northern Bida Basin, Central Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- A. Y. Jimoh, M. B. Saadu, A. A. Adetoro, J. Ajadi, T. Issa, U. Issa, Sedimentological and geochemical evaluation of sandstones of the Ilaro formation, Dahomey Basin, Southwestern Nigeria : Insights into paleoenvironments, provenance, and tectonic settings , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 1, February 2024
- Olusola J. Ojo, Suraju A. Adepoju, Ayodeji Awe, Kehinde A. Alalade, Patti formation shales at Agbaja Plateau: A geochemical window into the provenance and tectonic setting history of the Southern Bida Basin, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- K. A Haruna, J. K. Raji, A. Y. Jimoh, J. A. Adeoye, O. O. Alu, A. A. Badmus, B. Garba, Biostratigraphy and paleoenvironment studies of shales from Owan-1 Well, Niger Delta Basin, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Bethel Onyeka Ekute, Muluh Emmanuel Khan, Aloysius Akaangee Pam, Jude Ehwevwerhere Emurotu, Assessment of the nutritional and phytochemical composition of selected mushroom species grown in Southern Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- L. Guru Prasad, R. Ravikumar, R. Ganapathi Raman, R. Rajesh Kannad, Investigations on the structural, vibrational, optical and photocatalytic behavior of CuO, MnO and CuMnO nanomaterials , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- S. Iyakwari, H. J. Glass, G. K. Rollinson, A. A. Umbugadu, O. D. Opaluwa, B. O. Frankie, Validation of Near InfraRed preconcentration strategies for ore sorting , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- T. O Lawal, O. Fawale, J. A. Sunday, G. B. Egbeyale, Interpretation of airborne radiometric data of flamingo field, Southwestern Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 1, February 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Ibukun Akinsola, Aderemi Babatunde Alabi, Muibat A Soliu, Taiye Akomolafe, Optimization of Method and Components of Enzymatic Fuel Cells , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 1, Issue 4, November 2019






