Advance effect of magnetic field on the rheological properties of manganese zinc ferrite ferrofluid
Keywords:
Complex viscosity, Magnetization, Coercivity, ModulusAbstract
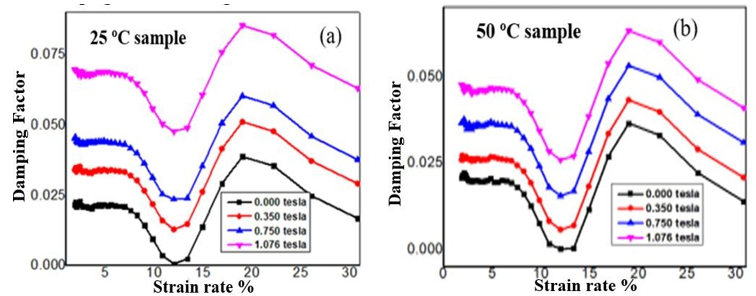
The rheological characteristics of manganese zinc (Mn-Zn) ferrite magnetic nanofluid synthesized using co-precipitation technique were examined in the absence and presence of magnetic fields. The research formulates required conditions needed for the formation of a gelly-like structure. The impact of magnetic field and temperature on the rheological properties of Mn-Zn ferrite ferrofluid is investigated. When a magnetic field was applied, higher magnetoviscoelasticity and magnetoviscosity were formed. Analysis was also done on other rheological parameters, such as the damping factor, which is crucial for regulating and restricting vibrations in a system. A stiff, gel-like structure is produced when a magnetic field is applied, and the gel-like quality grows as the magnetic field increases; when the magnetic field is removed, the gel-like and rigidity of the structure is lost. At low temperatures, the liquid phase is dominated by solid-like particles, whereas at high temperatures, the liquid-like structure is dominant. This study reveals the conditions required for the creation of high viscous effect and the viscoelastic behavior induced by the field offers important insights for optimizing the Mn-Zn ferrite ferrofluid for a range of applications. Other criterial for gel-like structure formation such as low torque and deflection angle of the ferrofluid were also established.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 A. A. Ibiyemi, O. Akinrinola, G. T. Yusuf, S. Olaniyan, J. Lawal, M. Orojo, B. Osuporu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- I. E. Otuokere, J. G. Ohwimu, K. C. Amadi, C. O. Alisa, F. C. Nwadire, O. U. Igwe, A. A. Okoyeagu, C. M. Ngwu, Synthesis, Characterization and Molecular Docking Studies of Mn (II) Complex of Sulfathiazole , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 1, Issue 3, August 2019
- Thirumalai A, Muthunagai K, Ritu Agarwal, Pre-functions and Extended pre-functions of Complex Variables , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 2, May 2023
- Terver Daniel, F. Eriba-Idoko, J. O. Tsor, S. T. Kungur, E. O. Enokela, F. Gbaorun, E. C. Hemba, A. A. McAsule, N. S. Akiiga, P. O. Ushie, Effects of Repeated Frying on Physical Properties of Cooking Oil obtained from Local Markets in Makurdi Metropolis, Benue State, Nigeria. , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- T. W. David, B. J. Adekoya, C. M. Michael, S. A. Adekoya, O. A. Adenuga, S. O. Kareem, H. T. Oladunjoye, A. E. Ajetunmobi, O. T. Williams, D. T. Ogundele, A Study of the Relationship Between Southward Bz > -10 nT and Storm Time Disturbance Index During Solar Cycle 23 , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- U. S. Aliyu, I. G. Geidam, M. S. Otto, M. Hussaini, Investigations of the Elastic Moduli of Er2O3 NPs Doped TeO2 – B2O3 – SiO2 Glasses using Theoretical Models , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- B. C. Asogwa, I. E. Otuokere, Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of Fe(II) and Cu(II) nano-sized complexes of sulfamethoxazole , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- F. C. Ugbe, O. E. Ominigbo, A. O. Akano, Tectonic Setting of the Syenite Around Igarra, Southwestern Nigeria: Constraints from Geochemistry , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Rachid El chaal, Hamid Dalhi, Otmane Darbal, Omar Boughaleb, Analytical resolution of nonlinear fractional equations using the GERDFM method: Application to nonlinear Schrödinger and truncated Boussinesq-Burgers equations , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Opeyemi O. Enoch, Catherine O. Alakofa , Lukman O. Salaudeen , Odd Order Integrator with Two Complex Functions Control Parameters for Solving Systems of Initial Value Problems , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- I Magaji, A Shuaibu, M. S Abubakar, M Isah, Effect of Substitutional Point Defect of Gold (Au) in Indium (In) Site of Double Halide Perovskite (Cs2InSbCl6) , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- A. A. Ibiyemi, G. T. Yusuf, O. Akirinola, M. Orojo, B. Osuporu, J. Lawal, Investigating the magnetic domain structure and photonics characters of Singled Phased hard ferromagnetic Ferrite MFe3O4 (M= Co2+, Zn2+, Cd2+) Compounds , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 1, February 2024






