Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles from Cucurbita maxima leaf extract; a platinum free counter electrode for dye sensitized solar cells
Keywords:
Green synthesis, DSSCs, CuO, Cucurbita maxima, Natural dyeAbstract
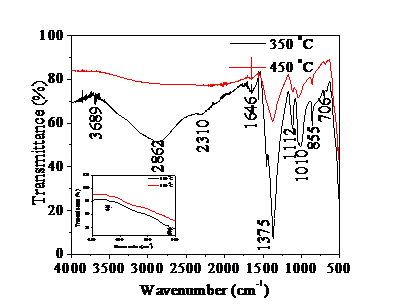
Green synthesis of metal oxides has attracted attention as the latest technology in synthesizing metal oxide nanoparticles due to its simplicity, cheapness, non-toxicity and its ability for large scale production. Metal oxides find applications in dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) as counter electrodes (CEs) and photo-anodes. However, applications of green synthesized metal oxides as counter electrodes have not been fully explored. In this study, CuO nanoparticles (NPs) were synthesized from Cucurbita maxima leaf extract and applied as a CE in DSSC. Uniformly synthesized CuO NPs were subjected to various characterization tools to obtain the crystal structure, surface morphology, particle size, optical properties, chemical bonds and photovoltaic properties. Using a natural dye from of Cucurbita maxima as a photon absorber, a short circuit current density ( Jsc) of 4.2 µA/cm2, open circuit voltage (Voc) of 0.17 V, a maximum power (Pmax) of 0.18 mW/cm2, and a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 1.8 × 10?4 % under one-sun illumination were obtained.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Emma Panzi Mukhokosi, Stephen Tenywa, Nandipha L. Bothab, Shohreh Azizi, Mathapelo Pearl Seopela, Malik Maaza

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- A. A. Willoughby, A. A. Soge, O. F. Dairo, O. D. Olukanni, E. U. Durugbo, W. S. Michael, T. A. Adebayo, Fabrication and Characterization of a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell using Natural Dye Extract of Rosella (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) as Photosensitizer , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- K. M. Omatolaa, A. D. Onojah, A. N. Amah, I. Ahemen, Synthesis and characterization of silica xerogel and aerogel from rice husk ash and pulverized beach sand via sol-gel route , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- Eli Danladi, Jamila Tasiu, Lucky Endas, Preparation and Characterization of High Performance Dye Sensitized Solar Cells with Silver Nanoparticles in nanocomposite Photoanode , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 2, Issue 1, February 2020
- Ibukun Akinsola, Alabi Aderemi Babatunde, Adedayo Kayode Seun, Nicola Coppede, Characterizations of Galena as Potential Photosensitizer in a Natural Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 2, May 2021
- L. O. Animasahun, B. A. Taleatu, S. A. Adewinbi, H. S. Bolarinwa, A. Y. Fasasi, Synthesis of SnO2/CuO/SnO2 Multi-layered Structure for Photoabsorption: Compositional and Some Interfacial Structural Studies , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 2, May 2021
- A. H. Labulo, A. D. Terna, O. F. Oladayo, H. Ibrahim, N. S. Tanko, R. A. Ashonibare, J. D. Opeyemi, Z. Tywabi-Ngeva, Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of green-mediated Khaya senegalensis-silver nanoparticles and oxidized carbon nanotubes , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 3, August 2023
- B. T. Iorhuna, T. T. Awuhe, I. C. Azuaga, E Isaac, F. Shuaibu, B. Yohanna, Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activities of Copper-Tea Leaves (Camellia Sinensis) Extract Nanoparticles.: None , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Bamidele H. Akpeji, Bulouebibo Lari, Ufuoma A. Igbuku, Godswill Tesi, Elias E. Elemike, Paul O. Akusu, Synthesis and Characterization of MnO2 nanoparticles mediated by Raphia hookeri seed , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 4, November 2024
- K. M. Omatola, A. D. Onojah, R. Larayetan, A. O. Ohiani, I. I. Oshatuyi, M. B. Ochang, O. Anawo, P. Abraham, Isolation and investigation of the structure of silicon quantum dots from rice husk ultrafine silica for possible applications in nanoelectromechanical systems , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Sathish Kumar Kannaiyan, Rengaraj R, Venkata krishnan G R, Gayathri P K, Lavanya G, Hemapriya D, Antimicrobial activity of green synthesized tri-metallic oxide Ni/Cr/Cu nanoparticles , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






