Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based model for pneumonia detection using chest x-ray images
Keywords:
Machine Learning , Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Artificial Intelligence, Pre-trained Models, Pneumonia DetectionAbstract
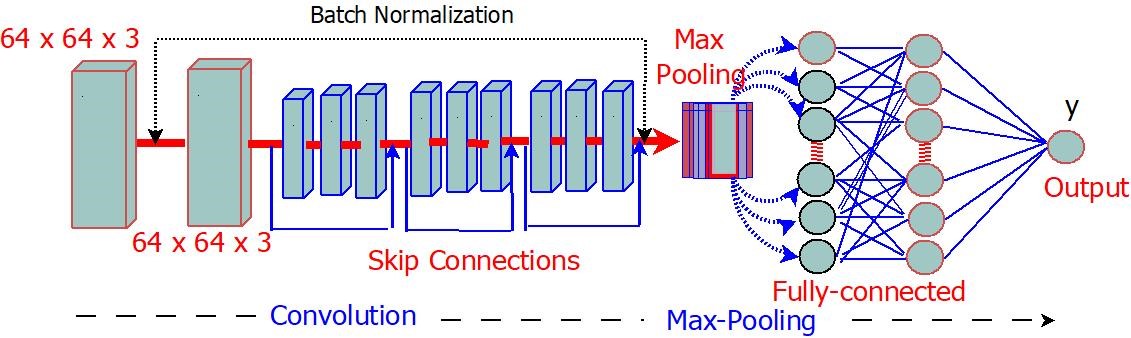
In recent years, the integration of machine learning techniques within the medical field has shown promising results in aiding healthcare pro[1]fessionals in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. This study focuses on developing and implementing a machine learning model tailored specifically for medical diagnosis, leveraging advancements in computer vision and deep learning algorithms. This research aims to design an efficient and accurate model capable of classifying medical images into distinct categories, enabling automated diagnosis and identification of various ailments and conditions. This study uses a dataset comprising 5,863 Chest X-ray images (JPEG) and 2 categories (Pneumonia/Normal) (anterior-posterior) selected from retrospective cohorts of pediatric patients of one to five years old from Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou, obtained from Kaggle data repositories. Data Preprocessing was conducted to enhance image quality and extract relevant features, followed by implementing a deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) model using TensorFlow’s Keras. Using pre-trained models such as Resnet, transfer learning techniques were employed to learn efficient features from large-scale datasets and optimize the model’s performance with the limited medical data available. The results from the experimental analysis showed that after 9 epochs, the training and validation accuracies had steadily increased, achieving 95% and 75%, respectively. Overall, the model achieved 99.9% training accuracy across multiple epochs and an average validation accuracy of 75%. The model’s performance and scalability highlight its potential for integration into clinical workflows. This could revolutionize healthcare by augmenting the diagnostic process and improving patient outcomes.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 S. I. Ele, U. R. Alo, H. F. Nweke, A. H. Okemiri, E. O. Uche-Nwachi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







