Waste glass: An excellent adsorbent for crystal violet dye, Pb2+ and Cd2+ heavy metals ions decontamination from wastewater
Keywords:
adsorption, waste glass, heavy metals, crystal violet dye, waste waterAbstract
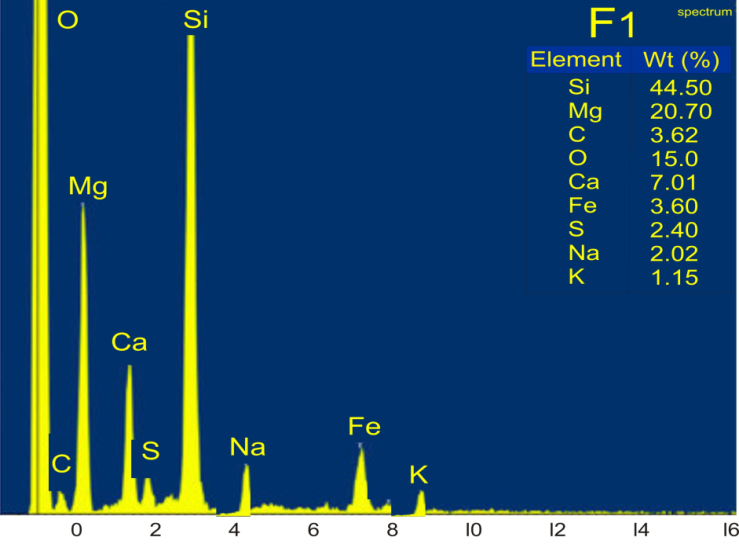
The suitability of waste glass as an eco-friendly adsorbent for the removal of crystal violet (CV) dye, Pb2+ and Cd2+ heavy metal ions in waste water samples was investigated in batch mode. Waste glass sample was pulverized and characterized by SEM/EDX, XRD, BET and FTIR. Effects of variation in temperature, pH, contact time and recyclability of the adsorbent were studied. FTIR spectra revealed major peaks around 491.53 and 3444.12 cm-1 corresponding to the bending vibrations of Si-O-Si and -OH groups respectively. SEM/EDX analysis showed a dense, coarse, porous morphology with predominantly silica component. The effective surface area and size of the adsorbent were 557.912 m2/g and 2.099 nm respectively. Increase in temperature, dosage, contact time resulted in increase in adsorption efficiency. Optimum adsorption efficiency of 94%, 97.5% and 89.1% was attained for Pb2+ , Cd2+ ions and CV dye respectively at 70?C. Adsorption process followed more accurately pseudo-first order model and isotherm fitted perfectly into Freundlich model indicating a multilayer adsorption mechanism for CV dye and the heavy metals. 89.87% reduction in Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) level of wastewater was reported upon treatment with waste glass adsorbent affirming its efficiency for dye and heavy metal pollutants removal.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Suha Ibrahim Salih Al-Ali, Zaidun Naji Abudi, Mohammed Nsaif Abbas, Modelling and Simulation for the use of Natural Waste to Purified Contaminated Heavy Metals , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- J. O. Coker, A. A. Rafiu, N. N. Abdulsalam, A. S. Ogungbe, A. A. Olajide, A. J. Agbelemoge, Investigation of Groundwater Contamination from Akanran Open Waste Dumpsite, Ibadan, South-Western Nigeria, using Geoelectrical and Geochemical Techniques , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 2, May 2021
- N. K. Olasunkanmi, D. T. Ogundele, V. T. Olayemi, W. A. Yahya, A. R. Olasunkanmi, Z. O. Yusuf, S. A. Aderoju, Assessing leachate contamination and groundwater vulnerability in urban dumpsites: a case study of the Ipata Area, Ilorin, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- Chinnarao Menda, Ch. Ramakrishna, V D N Kumar Abbaraju, Analysis of industrial solid waste for secure and eco-friendly disposal by incineration practices , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- E. O. Echeweozo, C. I. Nworie, A. O. Ojobeagu, P. B. Otah, I. J. Okoro, Health risk assessment due to environmental radioactivity and heavy metal contamination at the central solid waste dumpsite in Ebonyi State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- O. T. Fatunsin, O. F. Adeyeye, K. O. Olayinka, T. O. Oluseyi, Effect of pH on the Leaching of Potentially Toxic Metals from Different Types of Used Cooking Pots , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- S. A. Adesokan, A. A. Giwa, I. A. Bello, Removal of Trimethoprim from Water using Carbonized Wood Waste as Adsorbents , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- B. N. Hikon, G. G. Yebpella, L. Jafiya, S. Ayuba, Preliminary Investigation of Microplastic as a Vector for Heavy Metals in Bye-ma Salt Mine, Wukari, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- D. D. Bwede, R. A. Wuana, G. O. Egah, A. U. Itodo, E. Ogah, E. A. Yerima, A. I. Ibrahim, Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- C. J. Ajaelu, O. Oyedele, A. A. Ikotun, E. O. Faboro, Safranin O dye removal using Senna fistula activated biomass: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- K. O. Sodeinde, S. A. Animashaun, H. O. Adubiaro, Methods for the Detection and Remediation of Ammonia from Aquaculture Effluent: A Review , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023






