Environmental and health risk assessment of cadmium, zinc,iron, copper in crops and soil at Enugu State dumpsite
Keywords:
Heavy metals, Risk assessment, Telfairia occidentalis, food safetyAbstract
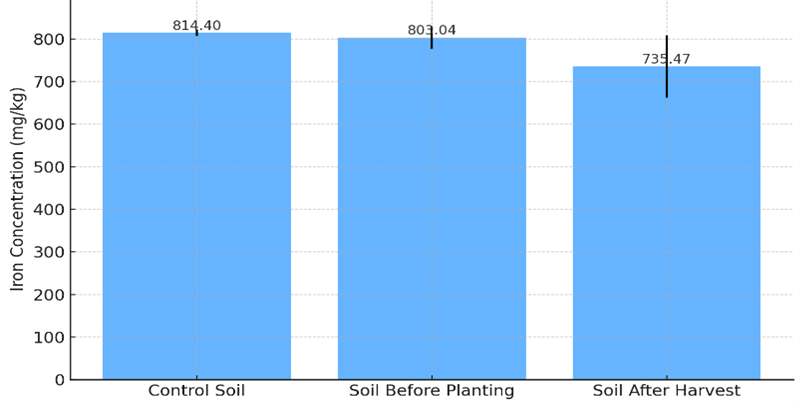
Contamination of soils and food crops around the Ugwuaji dumpsite in Enugu State, Nigeria was evaluated. Zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and cadmium (Cd) were determined in seventy-three (73) samples, which included pre-planting and post-harvest soils, control soils, ash from the New Artisan abattoir, and edible parts of Dioscorea bulbifera, Zea mays, and Telfairia occidentalis. Samples were digested with aqua regia and analyzed using atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). The analytical recovery was 96% with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 5.7%. Soil properties showed pH values between 5.2-6.7 (slightly acidic), cation exchange capacity (CEC) of 8.7-14.5 cmol/kg, and organic matter contents of 1.84-3.92%. Post-harvest soils recorded 11.33 ± 2.51 mg/kg higher concentrations of Zn and 4.64 ± 0.69 mg/kg of Cu compared to control soils, while Fe decreased to 735.47 ± 73.20 mg/kg. Cadmium was detected in one soil sample (1.14 mg/kg) and in T. occidentalis (0.02-2.03 mg/kg), but was not detected in D. bulbifera and Z. mays. Pollution indices revealed high Cd contamination with enrichment factor (EF > 10), geoaccumulation index (Igeo > 2), contamination factor (CF > 6), and a pollution load index (PLI) of 1.65. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) of Zn in T. occidentalis was 3.98 with a translocation factor (TF) of 1.87, showing strong accumulation. Estimated daily intake (EDI) and total hazard index (THI) for adults were low (0.00042-0.00057), while children showed high THI values of 4.28 for Z. mays and 4.54 for D. bulbifera. Structural equation modeling indicated that soil pH (? = -0.62) influenced Cd mobility and its accumulation in T. occidentalis (? = 0.58), contributing to child-specific health risk (? = 0.79). These results highlight the need for risk control measures, including regulated ash application and crop-specific monitoring in waste-affected farmlands.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Emmanuel Agboeze, Henry Okechukwu Agboeze, Theresa Orieji Uchechukwu, Anayo Vitus Ofordile, Chukwuebuka Gabriel Eze (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- M. A. Lala, S. Kawu, O. A. Adesina, J. A. Sonibare, Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution Status in Surface Soil of a Nigerian University , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- Godwin O. Olutona, Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediment of Tropical Freshwater Stream , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- D. D. Bwede, R. A. Wuana, G. O. Egah, A. U. Itodo, E. Ogah, E. A. Yerima, A. I. Ibrahim, Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- E. O. Echeweozo, C. I. Nworie, A. O. Ojobeagu, P. B. Otah, I. J. Okoro, Health risk assessment due to environmental radioactivity and heavy metal contamination at the central solid waste dumpsite in Ebonyi State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- J. A. Akinpelu, K. P. Ojo, S. O. Salawu, G. O. Olutona, F. O. Aweda, O. O. Jegede, Concentrations of heavy metal content in indoor dust and potential exposure in preschool children , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 8, Issue 1, February 2026
- N. K. Olasunkanmi, D. T. Ogundele, V. T. Olayemi, W. A. Yahya, A. R. Olasunkanmi, Z. O. Yusuf, S. A. Aderoju, Assessing leachate contamination and groundwater vulnerability in urban dumpsites: a case study of the Ipata Area, Ilorin, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- D. N. Ajah, E. Agboeze, J. N. Ihedioha, E. Chukwudi-Madu, C. C. Chime, Levels of Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), and Cadmium (Cd) in Soil, Rice Stalk, and Oryza Sativa Grain in Ishiagu Rice Field, Ebonyi State, Nigeria; Human Health Risk , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- B. N. Hikon, G. G. Yebpella, L. Jafiya, S. Ayuba, Preliminary Investigation of Microplastic as a Vector for Heavy Metals in Bye-ma Salt Mine, Wukari, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- B. O. Eyenubo, V. O. Peretomode, F. Egharevba, S. A. Osakwe, O. G. Avwioro, Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments and fish from dredged tributaries and creeks of river Ethiope, South-South, Nigeria: sources, risk assessment and bioaccumulation , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- O. F. Odubanjo, O. A. Falaiye, M. M. Orosun, M. Sanni, Investigation of particulate matter Air Quality Index (AQI) and risk assessment in some locations in Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 4, November 2024
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






