Analysis of Adenanthera pavonine L. (Febaceae) Pod and Seed as Potential Pyrolysis Feedstock for Energy production
Keywords:
Adenanthera pavonine; composition analysis, ultimate analysis; proximate analysis; kinetic, thermodynamicsAbstract
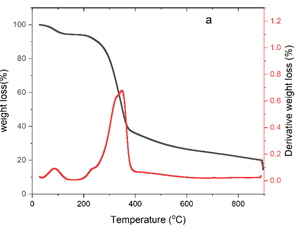
Though countless possible bioenergy feedstocks are available, the lack of information on their characteristics has made them unusable for industrial purposes. This study revealed the bioenergy potential of seed and pod of Adenanthera pavonine by analyzing their physicochemical, ultimate, proximate, kinetic, thermodynamic, thermal, and higher heat value. The seed presented 19.90%, 2.12%, 24.40% and 14.73% cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin and extractive respectively, while the pod has 21.35%, 25.15%, 23.50% and 11.63%. From the proximate analysis the pod has higher volatile matter (92.79%), and fixed carbon (1.40%), while the seed has higher moisture (6.36%), ash (0.84%), and higher heat value (18.63 MJ kg-1). The kinetic and thermodynamics results present the seed with Ea 23.73 kJmol-1, ?H 14.06 kJmol-1, ?G 10.74 kJmol-1 and ?S -78 Jmol-1, while the pod has 21.3 kJmol-1, ?H 12.20 kJmol-1, ?G 10.98 kJmol-1 and ?S -83 Jmol-1. The probable energy blockade between Ea and ?H for the seed and pod was 9.72. The high value of H: C and low O: C, with the higher heating values recorded for the pod and seed, presented them as better biofuel candidates. The study results have supplied necessary information for the industrial utilization of Adenanthera pavonine seed and pod as valuable feedstocks for bioenergy conversion.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Olayinka Oluwaseun Oluwasina, Mochamad Zakki Fahmi, Olugbenga Oludayo Oluwasina, Enhancing cellulose fiber properties from chromolaena odorata and anana comosus through novel pulping chemical mixtures , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024






