The corrosion characteristics of SS316L stainless steel in a typical acid cleaning solution and its inhibition by 1-benzylimidazole: Weight loss, electrochemical and SEM characterizations
Keywords:
Corrosion inhibitor, Stainless steel, Acid cleaning, Imidazole, PolarizationAbstract
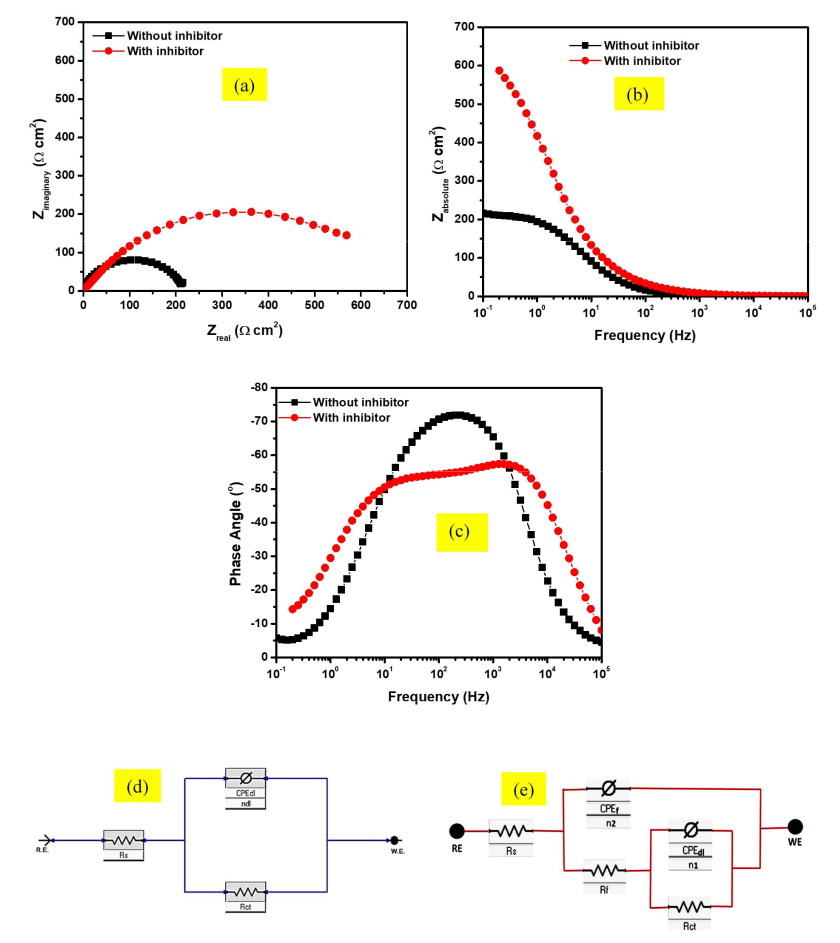
Acid cleaning, an inevitable industrial practice used to descale chemical reactors, usually causes serious corrosion attack on underlying alloy substrates. Ameliorating this phenomenon requires the addition of effective corrosion inhibitors into the acid solution. Current global regulations encourage environmentally–benign molecules as corrosion inhibitors. Consequently, 1-benzylimidazole has been investigated for its inhibitive characteristics against the corrosion of SS316L stainless steel in a typical acid cleaning solution containing 2 % HCl + 3.5 % NaCl. Weight loss measurements confirm that the corrosion inhibition property of 1-benzylimidazole increases with concentration but depreciates with increased temperature. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and potentiodynamic polarization (PDP) measurements confirm that 1-benzylimidazole adsorb on the stainless steel surface to isolate its surface from the acid solution. 1-benzylimidazole is a mixed-type inhibitor with greater anodic influence, and its adsorption enhances the formation and protectiveness of a passive film. Weight loss and the electrochemical measurements agree to an average inhibition efficiency > 70 % at 1000 ppm. The inhibitor adsorbs via physisorption and obeys the Temkin isotherm model. SEM surface characterization confirm the ability of 1-benzylimidazole to protect the surface microstructure of the stainless steel during the corrosion.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- C. B. Adindu, S. C. Nwanonenyi, C. B. C. Ikpa, Experimental and computational studies of the corrosion inhibitive effects of Zingiber officinale rhizomes on mild steel corrosion in acidic solutions , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 3, August 2023
- Yazid Amri, Mohammed Abdelkader Belalem, Nedjimi Mohammed Said, Guerguer Louiza, Salah Tlili, Corrosion inhibition of carbon steel XC70 in 1M HCl solution using Balanite Aegyptiaca extracts as an eco-friendly inhibitor , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Titus O. Martins, Edwin A. Ofudje, Abimbola A. Ogundiran, Ojo A. Ikeoluwa, Osipitan A. Oluwatobi, Ezekiel F. Sodiya, Opeyemi Ojo, Cathodic Corrosion Inhibition of Steel by Musa Paradisiaca Leave Extract , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Saprizal Hadisaputra, Lalu Rudyat Telly Savalas, Corrosion Inhibition Properties of Lawsone Derivatives againts Mild Steel: A Theoretical Study , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 3, August 2023
- Chidi Duru, Ijeoma Duru, Chiagoziem Chidiebere, Virtual Screening of Selected Natural Products as Human Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 Blockers , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- O. T. Fatunsin, O. F. Adeyeye, K. O. Olayinka, T. O. Oluseyi, Effect of pH on the Leaching of Potentially Toxic Metals from Different Types of Used Cooking Pots , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- B. T. Ogunyemi, F. K. Ojo, Corrosion Inhibition Potential of Thiosemicarbazide Derivatives on ALuminium: Insight from Molecular Modelling and QSARs Approaches , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Selvaraju Sivamani, Marwan Ahmed Sulieman Al Aamri, Aseela Musalem Awad Anthroon Jaboob, Azeezah Mohammed Masoud Kashoob, Layal Kamall Abdullah Al-Hakeem, Mouna Salim Mhaad Said Almashany, Muna Ahmed Mohammed Safrar, Heterogeneous Catalyzed Synthesis of Biodiesel from Crude Sunflower Oil , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- Olugbenga O. Oluwasina, Abiodun D. Aderibigbe, Damilola C. Petinrin, Adeyemi S. Adebisi, Olayinka O. Oluwasina, Oluwasegun J. Wahab, Potential of Anacardic Acid for Nanosized Cellulose Preparation Under Different Treatment Conditions , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- S. D. Umoh, A. K. Asekunowo, I. S. Okoro, N. X. Siwe, R. W. M. Kraus, O. O. Okoh, A. O. T. Ashafa, O. T. Asekun, O. B. Familoni, Antioxidant evaluation and bio-guided isolation from methanol leaf extract of Acalypha godseffiana , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






