Antioxidant evaluation and bio-guided isolation from methanol leaf extract of Acalypha godseffiana
Keywords:
Acalypha godseffiana, spectroscopy, antioxidant, antifungal, bioactive compoundsAbstract
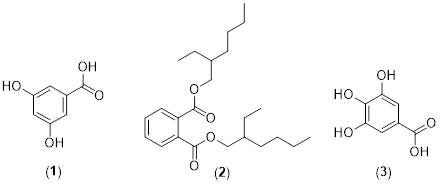
Acalypha godesffiana is a plant used in conventional medicine for fungal-related illnesses. The plant‘s extracts were investigated in this study, antioxidant, and antimicrobial studies were conducted. Different models were employed in the antioxidant assay; serial dilution was utilized to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The extract from A. godseffiana was purified and characterized by chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques, respectively. Three biologically active compounds, 3, 5-dihdroxylbenzoic acid (1), 3, 4, 5-trihydroxybenzoic acid (2), as well as Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (3), were identified for the first time in A. godseffiana. The extract and fractions exhibited varying scavenging capacities on different anti-oxidative models. The DPPH of MeOH (IC50= 0.51 mg mL^-1) was comparable with silymarine (SLY) IC50= 0.52 mg mL^-1 and better than gallic acid (GAL) IC50=1.95 mg mL^-1; the ABTS.+ of EtOAc column fraction (ACF, IC50=0.46 mg mL^-1) was comparable with standard SLY, IC50 = 0.47 mg mL^-1; and an OH radical of DCM, IC50= 0.10 mg mL^-1, was better than both standards (SLY, IC50= 6.30 mg mL^-1, GAL: IC50= 1.93 mg mL^-1). ACF showed superior antifungal activities (0.02 mg mL^-1) against Cryptococcus neoformans and Candida albicans, compared to ketoconazole (MIC of 0.250 mg mL^-1). Compounds (1-3) from A. godseffina reportedly displayed antioxidant and other activities. This study validated the antifungal potentials of A. godseffiana leaves and identified bioactive compounds. The extracts should be further investigated, and the compounds should be added to the existing library for further investigation of possible leads.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 S. D. Umoh, A. K. Asekunowo, I. S. Okoro, N. X. Siwe, R. W. M. Kraus, O. O. Okoh, A. O. T. Ashafa, O. T. Asekun, O. B. Familoni

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Sathish Kumar Kannaiyan, Rengaraj R, Venkata krishnan G R, Gayathri P K, Lavanya G, Hemapriya D, Antimicrobial activity of green synthesized tri-metallic oxide Ni/Cr/Cu nanoparticles , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- S. A. Adesokan, A. A. Giwa, I. A. Bello, Environmental, Health and Economic Implications of Emerging Contaminants in Nigeria Environment , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- A. F. Afolabi, S. S. Oluyamo, I. A. Fuwape, Synthetic Characterization of Cellulose from Moringa oleifera seeds and Potential Application in Water Purification , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- S. Iyakwari, H. J. Glass, G. K. Rollinson, A. A. Umbugadu, O. D. Opaluwa, B. O. Frankie, Validation of Near InfraRed preconcentration strategies for ore sorting , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- K. M. Omatola, A. D. Onojah, R. Larayetan, A. O. Ohiani, I. I. Oshatuyi, M. B. Ochang, O. Anawo, P. Abraham, Isolation and investigation of the structure of silicon quantum dots from rice husk ultrafine silica for possible applications in nanoelectromechanical systems , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






