Mathematical advection-diffusion model of primary and secondary pollutants emitted from the point source with mesoscale wind and removal mechanisms
Keywords:
Mesoscale winds, Eddy diffusivity, Removal mechanism, Gravitational settling velocity, Leakage velocity and Finite difference techniqueAbstract
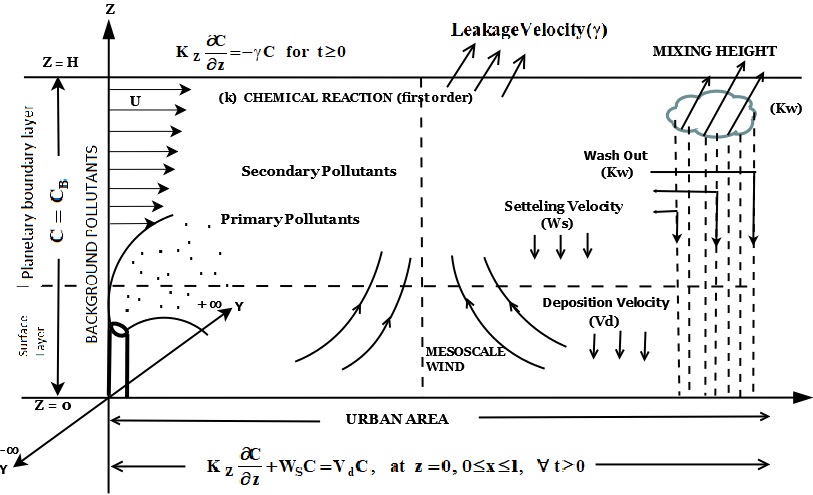
A numerical model is represented to study the effect of gravitational settling velocity and leakage velocity on the concentration distribution of primary and secondary pollutants emitted from the point source in an urban area with mesoscale wind. The point source characterizes pollutants emission from industrial process stacks and fuel combustion facility stacks. The article deals with the dispersion of primary and secondary pollutants emitted from point source with mesoscale wind along with large scale wind. The Crank-Nicolson's implicit finite difference method is adopted for solving partial differential equations of contaminant with wind velocity and eddy diffusivity profiles. Pollutants concentration been analysed for various removal mechanisms under stable as well as neutral condition of atmosphere. The results reveal decrease in the concentration of primary and secondary air contaminant by increasing the various removal mechanisms. In neutral condition the magnitude of concentration is less for the pollutants as compared with stable condition of atmosphere.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Vanita R. Raikar, Lakshminarayanachari K, K. Bharathi, C. Bhaskar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- R. Latha, K. Lakshminarayanachari, C. Bhaskar, An analytical model for point source pollutants in an urban area with mesoscale wind and wet deposition , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 4, November 2024







