Comprehensive study of photon and proton interactions to interpret the radiation parameters of boron derivative drugs for chemoradiotherapy
Keywords:
Boron derivative drugs, Chemoradiotherapy, Radiation parameter, Effective atomic numberAbstract
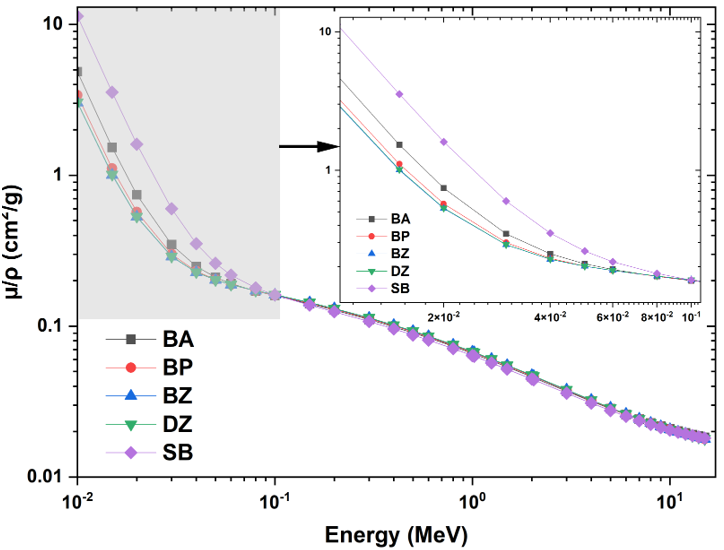
For chemoradiotherapy applications, this work investigated the photon and proton interaction parameters in five boron-based medications: sodium borocaptate, bortezomib, delanzomib, boronophenylalanine, and boric acid. Photon interaction parameters such as the mass attenuation coefficient, effective atomic number, effective electron density, and buildup variables were computed. The effective atomic number and stopping power for proton interactions were determined by calculating mass stopping cross-sections, which allowed for the computation of the effective electron density. Below 0.1 MeV, the highest value of mass attenuation coefficient and effective atomic number was found for sodium borocaptate and boric acid, respectively. Among the medications, boric acid had the highest effective atomic number for proton interactions. Both photon and proton interactions showed a direct correlation between electron density and effective atomic number. In the areas where medication variations were most noticeable, bortezomib showed the highest values for buildup factors. The mass stopping power and mass stopping cross-section peaked at about 0.1 MeV, with delanzomib and bortezomib exhibiting especially high values at lower energies. This study is expected to provide understanding about the radiation interaction parameters of the investigated boron derivative drugs, which will in turn guide their administration and effectiveness in enhancing photon and proton radiations for chemoradiotherapy purposes.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 A. M. Olaosun, C. A. Aborisade, D. E. Shian, P. T. Osuolale

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






