Analysis of the Bioactive Compounds from Carica papaya in the Management of Psoriasis using Computational Techniques
Keywords:
Psoriasis, Carica Papaya, Molecular docking, Anti-inflammatory, Skin disorderAbstract
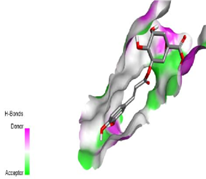
Psoriasis is a persistent and mysterious autoimmune skin condition that affects 2-3% of the world’s population. Currently, topical therapies, light therapy, and systemic drugs are the three main forms of treatment used to lessen inflammation and skin irritation/itching. However, all these treatments are only used to manage the disease each time it surfaces. Therefore, the main target of this work is to search for a safer and more effective remedy for psoriasis from the reservoir of phytochemicals present in Carica papaya via in silico studies due to its anti-psoriatic and anti-inflammatory properties. Reported phytochemicals isolated from Carica papaya were subjected to computational simulations using the PyRx docking tool and were docked against Janus Kinase 1 (JAK1) and Tumor necrosis factor \aplha (TNF\aplha) target receptors. The results obtained were visualized using PyMol, and Biovia 2019. Analysis of the results identified both Chlorogenic acid and Coumaroylquinic-acid with docking scores (-8.6 kcal/mol and -7.9 kcal/mol) respectively as potential inhibitors for the JAK1 receptor. The identified compounds also possessed excellent ADMET, drug-likeness, bioactivity, and activity spectra for substances (PASS) prediction properties. Their binding mode and the molecular interactions with the targets also affirmed their potency. In comparison with the standards (Methotrexate and Cyclosporine), Chlorogenic acid and Coumaroylquinic-acid have better ADMET properties, binding affinities, drug-likeness, PASS properties, bioactivities, oral bioavailability, binding mechanism, and interactions with the active site of the target receptor and are hereby recommended for further analysis towards the development of a new therapeutic agent for psoriasis treatment and management.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2023 Misbaudeen Abdul-Hammed, Ibrahim Olaide Adedotun, Tolulope Irapada Afolabi Afolabi, Ubeydat Temitope Ismail, Praise Toluwalase Akande, Balqees Funmilayo Issa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- G. Kamarajan, D. Benny Anburaj, V. Porkalai, A. Muthuvel, G. Nedunchezhian, Effect of temperature on optical, structural, morphological and antibacterial properties of biosynthesized ZnO nanoparticles , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- Faik Mayah, Nisreen Alokbi, Ali Sabeeh Rasheed, New Invariant Quantity To Measure The Entanglement In The Braids , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Constantin Falk, Tarek El Ghayed , Ron van de Sand, Jörg Reiff-Stephan, A Data-Driven Approach Towards the Application of Reinforcement Learning Based HVAC Control , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Umaru Hassan, Mohd Tahir Ismail, Improving forecasting accuracy using quantile regression neural network combined with unrestricted mixed data sampling , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- A. H. Labulo, A. D. Terna, O. F. Oladayo, H. Ibrahim, N. S. Tanko, R. A. Ashonibare, J. D. Opeyemi, Z. Tywabi-Ngeva, Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of green-mediated Khaya senegalensis-silver nanoparticles and oxidized carbon nanotubes , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 3, August 2023
- O. S. Oguntoye, A. M. Okooboh, O. M. Bello, A. H. Usman, S. S. Abdussalam, G. V. Awolola, Antimicrobial Assessment of Different Solvent Extracts of the Root-bark, Stem-bark and Leaves of Acacia ataxacantha Linn. , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 1, Issue 1, February 2019
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






