Virtual Screening of Selected Natural Products as Human Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 Blockers
Keywords:
Human tyrosinase-related protein 1, skin lightening, Hydroquinone, Tropolone, SalicinAbstract
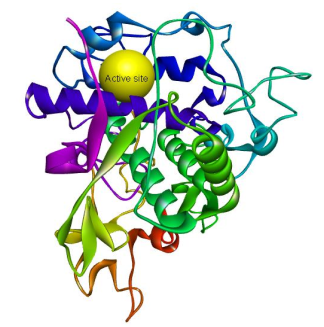
Many researchers have widely explored the need to replace the harmful compound hydroquinone in skin-lightening creams with more skin-friendly compounds that can give similar results. Some compounds from the plant kingdom have been shown to possess human tyrosinase inhibitory action with no adverse effect on the skin. In this study, the virtual screen of glabridin, kojic acid, arbutin, niacinamide, ascorbic acid, salicin, lactic acid, glutathione, azelaic acid, linoleic acid, glycolic acid, acclaimed to possess this activity as well as the synthetic compound hydroquinone, as human tyrosinase-related protein 1 inhibitor was investigated using computational methods. Site-directed docking was performed at the binding pocket on the enzyme carrying the cocrystallized ligand tropolone. The binding affinity of salicin (-6.7 kcal/mol), a-arbutin (-6.3 kcal/mol), glutathione (-6.2 kcal/mol), ascorbic acid (-5.7 kcal/mol), and niacinamide (-5.7 kcal/mol) were higher than that of the cocrystallized ligand tropolone (-5.5 kcal/mol) and the synthetic skin lightening compound hydroquinone (-4.8 kcal/mol). a-arbutin and glutathione also interacted with similar amino acids units as hydroquinone, suggesting that they followed the exact mechanism of action. These findings strongly corroborate the claim that these natural products could inhibit melanin production and may serve to replace hydroquinone in skin lightening creams.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2021 Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- S. Ponsadai Lakshmi, R. Deepa, S. Ganapathy Sankari, M. Jeyachandran, Pollution Status of Groundwater Resources Through Hydrochemical Characteristics - A Case Study From Southern India , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Bolarinwa Bolaji, Abdullahi Ibrahim, Favour Ani, Benjamin Omede, Godwin Acheneje, A model for the control of transmission dynamics of human monkeypox disease in Sub-Saharan Africa , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- Nassima Bou-ydia, Ben-issa El miraoui, Latifa Laallam, Ahmed Jouaiti, Interaction of hydroxyapatite and chitosan with gentamicin and their antimicrobial activities: DFT and molecular docking approach , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Josephine E. Ochigbo, Joel N. Ndam, Wipuni U. Sirisena, Optimal control with the effects of ivermectin and live stock availability on malaria transmission , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- B. J. Adekoya, B. O. Adebesin, V. U. Chukwuma, S. J. Adebiyi, S. O. Ikubanni, H. T. Oladunjoye, E. O. Adekoya, Pattern and variation of electron ionisation gradient as related to the plasma distribution mechanisms during the total solar eclipse of March 20, 2015 , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- Misbaudeen Abdul-Hammed, Ibrahim Olaide Adedotun, Tolulope Irapada Afolabi Afolabi, Ubeydat Temitope Ismail, Praise Toluwalase Akande, Balqees Funmilayo Issa, Analysis of the Bioactive Compounds from Carica papaya in the Management of Psoriasis using Computational Techniques , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- B. O. Eyenubo, V. O. Peretomode, F. Egharevba, S. A. Osakwe, O. G. Avwioro, Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in sediments and fish from dredged tributaries and creeks of river Ethiope, South-South, Nigeria: sources, risk assessment and bioaccumulation , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 2, May 2024
- M. Ramanuja, J. Kavitha, A. Sudhakar, N. Radhika, Study of MHD SWCNT-Blood Nanofluid Flow in Presence of Viscous Dissipation and Radiation Effects through Porous Medium , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- D. D. Bwede, R. A. Wuana, G. O. Egah, A. U. Itodo, E. Ogah, E. A. Yerima, A. I. Ibrahim, Characterization and Evaluation of Human Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Tin Mine Tailings in Selected Area of Plateau State, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- Matthew Iseh, Anthony Usoro, Nsisong Ekong, Idara Ukpe, Juxtaposing Vertically Transmitted Infections (VTIs) and the Spread of HIV/AIDS in a Typically Infection Prevalent Region in Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- C. E. Duru, C. E. Enyoh, I. A. Duru, M. C. Enedoh, Degradation of PET Nanoplastic Oligomers at the Novel PHL7 Target:Insights from Molecular Docking and Machine Learning , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023






