Air quality prediction enhanced by a CNN-LSTM-Attention model optimized with an advanced dung beetle algorithm
Keywords:
Air quality prediction, DBO, CNN, LSTM, AttentionAbstract
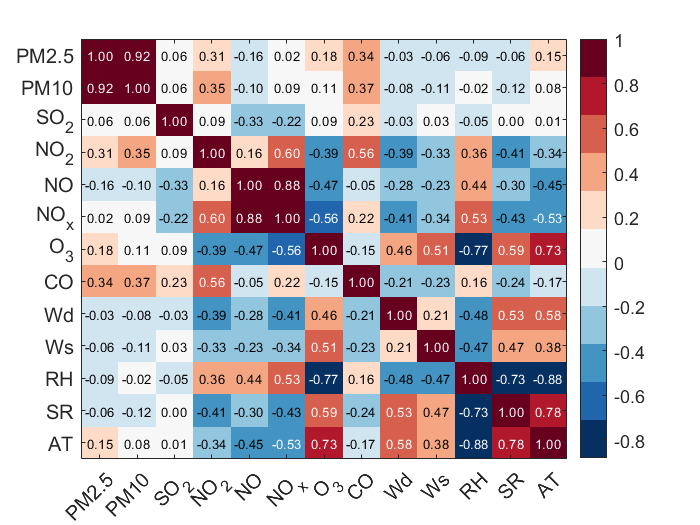
Air pollution significantly impacts human health and socioeconomic development, making accurate air quality prediction crucial. This study proposes a hybrid CNN-LSTM-Attention model optimized with an improved Dung Beetle Optimization (IDBO) algorithm to enhance predictive performance. IDBO integrates multiple strategies to improve global search capabilities and overcome the limitations of conventional DBO. Experiments using PM2.5 data from Penang, Malaysia, demonstrate that the proposed model outperforms other models across multiple evaluation metrics R2 = 0.904, RMSE = 2.677, MSE = 7.168, MAE = 1.982, MAPE = 44.1% The findings validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in improving air quality prediction, offering valuable insights for environmental monitoring and pollution control.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 xiaojie zhou, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Farah Aini Abdullah, Lili Wu, Ying Tian, Tao Li, Kaihui Li

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Mokhtar Ali, Abdelkerim Souahlia, Abdelhalim Rabehi, Mawloud Guermoui, Ali Teta, Imad Eddine Tibermacine, Abdelaziz Rabehi, Mohamed Benghanem , A robust deep learning approach for photovoltaic power forecasting based on feature selection and variational mode decomposition , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- O. F. Odubanjo, O. A. Falaiye, M. M. Orosun, M. Sanni, Investigation of particulate matter Air Quality Index (AQI) and risk assessment in some locations in Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 4, November 2024
- Lek Ming Lim, Yang Lu, Ahmad Sufril Azlan Mohamed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Data safety prediction using YOLOv7+G3HN for traffic roads , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- P. O. Odion, M. N. Musa, S. U. Shuaibu, Age Prediction from Sclera Images using Deep Learning , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 3, August 2022
- O. Oderinde, C. L. Mgbechidinma, A. O. Agbeja, A. A. Ajayi, A. O. Ogundiran, O. O. Olaide, O. A. Orelaja, C. A. Mgbechidimma, C. O. Ajanaku, K. D. Oyeyemi, Appraising raw exhaust pollutant gases emissions from industrial generators using statistics and machine learning approaches , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Y. B. Lawal, E. T. Omotoso, Investigation of Point Refractivity Gradient and Geoclimatic Factor at 70 m Altitude in Yenagoa, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- S. S. Aladodo, C. O. Akoshile, J. O. Otu, A Review of Evidence of Aerosol Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Particles , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- Anas Sani Maihulla, Ibrahim Yusuf, Performance Analysis of Photovoltaic Systems Using (RAMD) Analysis , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 3, August 2021
- S. I. Ele, U. R. Alo, H. F. Nweke, A. H. Okemiri, E. O. Uche-Nwachi, Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based model for pneumonia detection using chest x-ray images , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- Paavithashnee Ravi Kumar, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Olayemi Joshua Ibidoja, Identifying heterogeneity for increasing the prediction accuracy of machine learning models , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- O. J. Ibidoja, F. P. Shan, Mukhtar, J. Sulaiman, M. K. M. Ali, Robust M-estimators and Machine Learning Algorithms for Improving the Predictive Accuracy of Seaweed Contaminated Big Data , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- Shaymaa Mohammed Ahmed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Raja Aqib Shamim, Integrating robust feature selection with deep learning for ultra-high-dimensional survival analysis in renal cell carcinoma , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Paavithashnee Ravi Kumar, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Olayemi Joshua Ibidoja, Identifying heterogeneity for increasing the prediction accuracy of machine learning models , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- Nahid Salma, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Raja Aqib Shamim, Machine learning-based feature selection for ultra-high-dimensional survival data: a computational approach , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Raja Aqib Shamim, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Optimizing discrete dutch auctions with time considerations: a strategic approach for lognormal valuation distributions , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 1, February 2025
- Shaymaa Mohammed Ahmed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Arshad Hameed Hasan, Evaluating feature selection methods in a hybrid Weibull Freund-Cox proportional hazards model for renal cell carcinoma , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Raja Aqib Shamim, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Mohamed Farouk Haashir bin Hamdullah, Computational optimization of auctioneer revenue in modified discrete Dutch auctions with cara risk preferences , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 8, Issue 1, February 2026
- Chuchu Liang, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Lili Wu, A novel multi-class classification method for arrhythmias using Hankel dynamic mode decomposition and long short-term memory networks , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- Ibrahim Adamu Mohammed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Sani Rabiu, Raja Aqib Shamim, Shahida Shahnawaz, Development and validation of hybrid drying kinetics models with finite element method integration for black paper in a v-groove solar dryer , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- xiaojie zhou, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Farah Aini Abdullah, Lili Wu, Ying Tian, Tao Li, Kaihui Li, Implementing a dung beetle optimization algorithm enhanced with multi-strategy fusion techniques , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025






