Artificial potential field path length reduction using Kenneth-Nnanna-Saleh algorithm
Keywords:
Path planning, Artificial potential field, Obstacle avoidanceAbstract
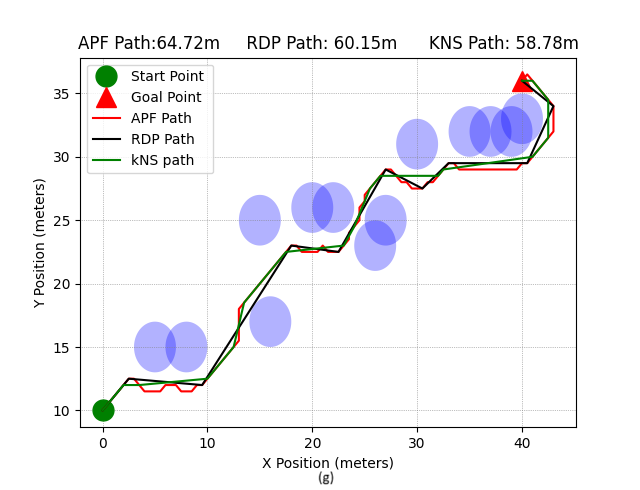
The artificial potential field (APF) is one of the famous path planning algorithms. It creates a virtual force field that attracts a robot to the goal or repels it from an obstacle, forcing it to move along the direction of the resultant forces toward the goal. The repulsive force pushes the robot away from the obstacle, causing a large displacement from the straight path, increasing the path length. This paper presents the Kenneth-Nnanna-Saleh (KNS) algorithm that can shorten the length of an APF path by reducing its waypoints. The algorithm takes an APF path that is generated from the problem domain as input, evaluates angles at each point, and compares the angle with a pre-defined threshold angle to remove or retain the point in the resultant KNS path. Simulation environments, each with varying complexity in obstacle arrangement, were designed for various simulations of the proposed algorithm. A Python-based computer simulation program was implemented and used to simulate the KNS, APF, and a similar waypoint reduction algorithm -Ramer-Douglas-Peucker (RDP) and the results were analyzed. The results show that KNS can yield a shorter path than APF and RDP and retain the obstacle avoidance feature of the path. The shortened path maintains the geometry of the APF path and leads to reduced energy cost for the deployment of robots.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Kenneth Christopher Ugwoke, Nnanna Nwojo Agwu, Saleh Abdullahi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Ebere Uzoka Chidi, Edward Anoliefo, Collins Udanor, Asogwa Tochukwu Chijindu, Lois Onyejere Nwobodo, A blind navigation guide model for obstacle avoidance using distance vision estimation based YOLO-V8n , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 1, February 2025
- S. I. Ele, U. R. Alo, H. F. Nweke, A. H. Okemiri, E. O. Uche-Nwachi, Deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based model for pneumonia detection using chest x-ray images , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- Mokhtar Ali, Abdelkerim Souahlia, Abdelhalim Rabehi, Mawloud Guermoui, Ali Teta, Imad Eddine Tibermacine, Abdelaziz Rabehi, Mohamed Benghanem , A robust deep learning approach for photovoltaic power forecasting based on feature selection and variational mode decomposition , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- T. S. Fagbemigun, M. O. Olorunfemi, S. A. Wahab, Modeling of Self Potential (SP) Anomalies over a Polarized Rod with Finite Depth Extents , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 1, Issue 2, May 2019
- Akindeji Opeyemi Fajana, Adam Muhammed Olawale, Hammed Ajibola Oyesomi, Quantitative reservoir evaluation and hydrocarbon volumetrics :an integrated petrophysical and 3-D static modeling approach in ‘Hamphidex’ field, Niger-Delta, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- B. M. Dyavappa, Energy distribution of an ion cloud in a quadrupole Penning Trap , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 2, Issue 2, May 2020
- Dyavappa B M, Velocity distribution of 43Ca+ion cloud in the low temperature limit in a quadrupole Penning Trap , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 1, February 2021
- Arezu Jahanshir, Jalil Naji, Relativistic correction on bottomia within the gaussian basis function method , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- B. M. Dyavappa, Higher order Motional Resonances Spectra of electrons with Non-linear Axial Oscillations in Quadrupole Penning trap , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- D. N. Ajah, E. Agboeze, J. N. Ihedioha, E. Chukwudi-Madu, C. C. Chime, Levels of Zinc (Zn), Copper (Cu), Iron (Fe), and Cadmium (Cd) in Soil, Rice Stalk, and Oryza Sativa Grain in Ishiagu Rice Field, Ebonyi State, Nigeria; Human Health Risk , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






