Synergistic intelligence: a novel hybrid model for precision agriculture using k-means, naive Bayes, and knowledge graphs
Keywords:
Hybrid knowledge discovery, Precision agriculture, K-means clustering, Knowledge graphsAbstract
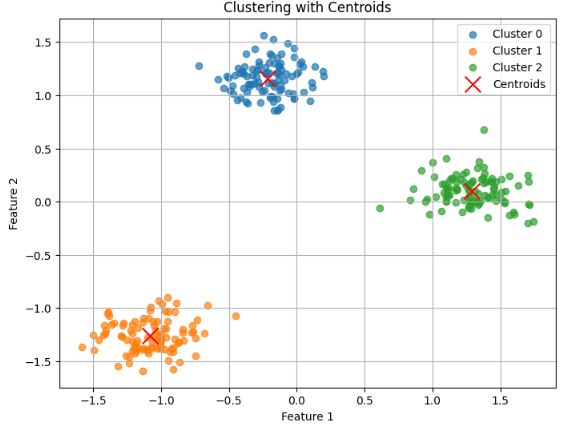
This study presents a novel hybrid knowledge discovery model integrating K-Means clustering, Naive Bayes classification, and Knowledge Graph technology to address interpretability and data heterogeneity challenges in precision agriculture. The proposed framework first applies K-Means to segment agro-ecological zones using multi-source data (soil, climate, satellite imagery), then employs Naive Bayes to classify crop productivity tiers, achieving 89% accuracy—surpassing standalone benchmarks (Naive Bayes: 86%, Random Forest: 87.5%). A Neo4j-based Knowledge Graph contextualizes these outputs, demonstrating 95% schema completeness and efficient querying (0.1559s latency), while enabling dynamic analysis of soil-climate-crop relationships. Pilot trials confirmed actionable impacts, including 22% reduced water use and 18% less fertilizer waste in targeted farms. By unifying unsupervised/supervised learning with semantic reasoning, this work advances scalable, interpretable decision support systems for sustainable agriculture, offering a replicable template for global food security initiatives.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2025 Catherine N. Ogbizi-Ugbe, Osowomuabe Njama-Abang, Samuel Oladimeji, Idongetsit E. Eteng, Edim A. Emanuel (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- A. K. Usman, Y. A. Hassan, A. A. Bery, A. S. Akingboye, M. D. Dick, B. M. Ahmed, R. O. Aderoju, Hybrid deep belief network and fuzzy clustering approach for geothermal prospectivity mapping in northeastern Nigeria using magnetic and landsat data , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 8, Issue 1, February 2026
- O. E. Ojo, M. K. Kareem, O. Samuel, C. O. Ugwunna, An Internet-of-Things based Real-time Monitoring System for Smart Classroom , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 2, May 2022
- Shaymaa Mohammed Ahmed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Raja Aqib Shamim, Integrating robust feature selection with deep learning for ultra-high-dimensional survival analysis in renal cell carcinoma , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- Shehu Magawata Shagari, Danlami Gabi, Nasiru Muhammad Dankolo, Noah Ndakotsu Gana, Countermeasure to Structured Query Language Injection Attack for Web Applications using Hybrid Logistic Regression Technique , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 4, November 2022
- Nahid Salma, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Raja Aqib Shamim, Machine learning-based feature selection for ultra-high-dimensional survival data: a computational approach , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Y. B. Lawal, E. T. Omotoso, Investigation of Point Refractivity Gradient and Geoclimatic Factor at 70 m Altitude in Yenagoa, Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 1, February 2023
- xiaojie zhou, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Farah Aini Abdullah, Lili Wu, Ying Tian, Tao Li, Kaihui Li, Implementing a dung beetle optimization algorithm enhanced with multi-strategy fusion techniques , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 2, May 2025
- B. Bako, E. E. Etim, J. P. Shinggu, S. S. Humphrey, L. J. Moses, M. E. Khan, Quantum chemical calculations of lupeol (C30H50O) isolated from the ethyl acetate leaf extracts of Justicia Secunda , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- Elsayed Elshoubary, Effect of reduction method on the performance a software defined network system using Gumbel Hougaard family copula distribution , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- Osowomuabe Njama-Abang, Denis U. Ashishie, Paul T. Bukie, Addressing class imbalance in lassa fever epidemic data, using machine learning: a case study with SMOTE and random forest , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Osowomuabe Njama-Abang, Denis U. Ashishie, Paul T. Bukie, Addressing class imbalance in lassa fever epidemic data, using machine learning: a case study with SMOTE and random forest , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025






