Quantitative reservoir evaluation and hydrocarbon volumetrics :an integrated petrophysical and 3-D static modeling approach in ‘Hamphidex’ field, Niger-Delta, Nigeria
Keywords:
Lithology, Net-to-gross, Hydrocarbon saturation, Hydrocarbon reservesAbstract
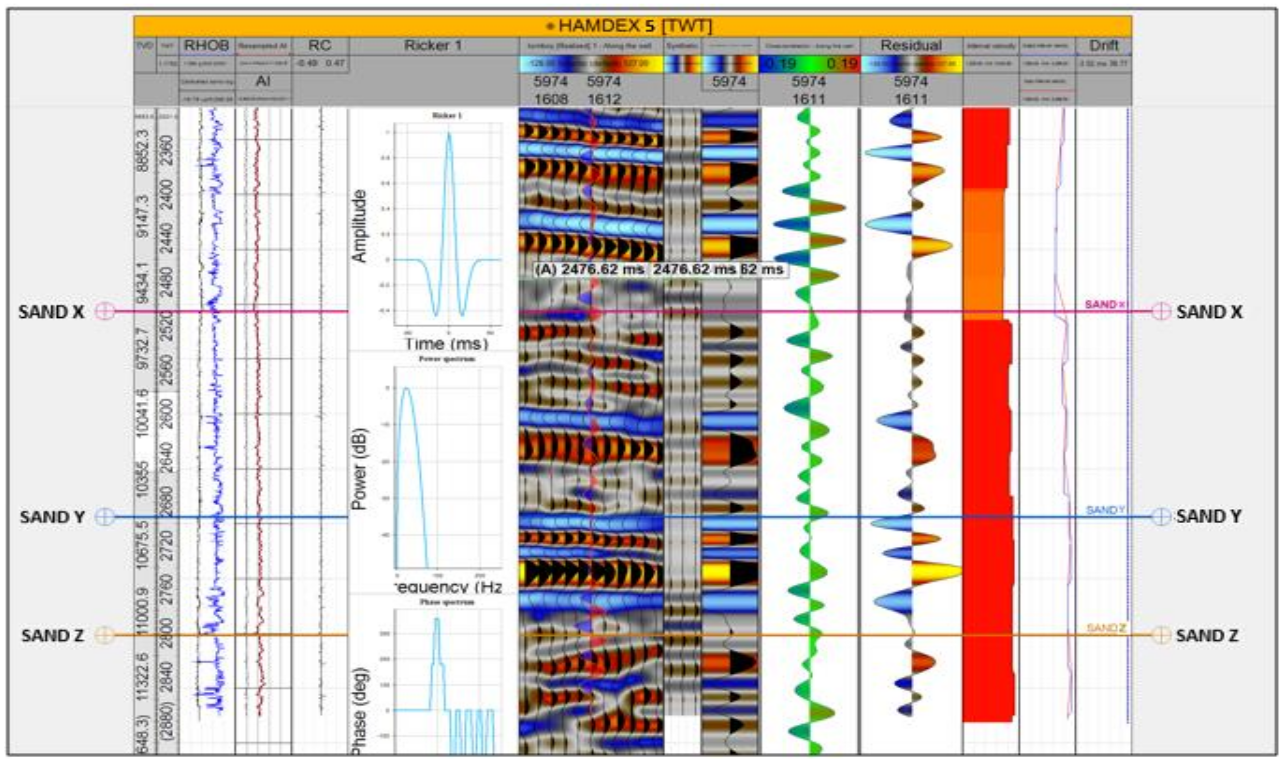
The viability and hydrocarbon volumetrics of the Hamphidex field reservoirs were evaluated using petrophysical analysis and three-dimensional (3D) static modeling of three key reservoir sands (X, Y, and Z). The petrophysical analysis involved detailed characterization of lithologies, net-to-gross ratios, porosity, hydrocarbon saturation, water saturation, and permeability. The volumetric attributes of the field were derived from the constructed 3D reservoir models. Two geostatistical methods—Sequential Gaussian Simulation (SGS) and Sequential Indicator Simulation (SIS)—were utilized for facies and property modeling, focusing on porosity and permeability. Comprehensive facies models and petrophysical property models were developed for each reservoir sand (X, Y, and Z), integrating 3D visualizations of facies distributions, porosity, permeability, water saturation, and fluid contact models. These models also included cross-sectional views, providing a detailed spatial representation of the reservoir's characteristics. Two main facies, sand and shale, were identified, with sand acting as the hydrocarbon reservoir. Well-log correlations in six wells (Hamdex-02, 06, 01, 05, 04 and 07) of the field show that sands X, Y, and Z have lateral continuity and their hydrocarbon potential varies between wells. Specifically, Sand ‘X’ contains hydrocarbons in Hamdex-05 and Hamdex-07, Sand ‘Y’ is hydrocarbon-rich in Hamdex-05, and Sand ‘Z’ shows hydrocarbon presence in Hamdex-06, Hamdex-05, and Hamdex-04. These hydrocarbons are confined within an anticlinal structural trap that closes on a fault. For Sand X, Y, and Z, porosity values range between 16 and 25%, permeability varies from 10 to 1600 mD, water saturation lies within 7 to 50%, and hydrocarbon saturation spans from 50 to 93%. The volumetric assessments from the build models showed that Sand X, Y and Z have Stock-Tank-Oil-Initially-In-Place (STOIIP) of 75.864, 8.566 and 80.177 Million Barrels (MMbbl) respectively. In addition to Sand Y STOIIP it also has Gas-Initially-In-Place (GIIP) of 14.870 Billion Standard Cubic Feet (Bscf). The analysis indicates that the field contains substantial hydrocarbon reserves, with the petrophysical properties confirming the reservoirs' high quality. These findings demonstrate that the field is economically viable and suitable for development, presenting a strong potential for successful exploitation.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Copyright (c) 2024 Akindeji Opeyemi Fajana, Adam Muhammed Olawale, Hammed Ajibola Oyesomi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Similar Articles
- Paavithashnee Ravi Kumar, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Olayemi Joshua Ibidoja, Identifying heterogeneity for increasing the prediction accuracy of machine learning models , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 3, August 2024
- Shaymaa Mohammed Ahmed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Arshad Hameed Hasan, Evaluating feature selection methods in a hybrid Weibull Freund-Cox proportional hazards model for renal cell carcinoma , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 3, August 2025
- Umaru Hassan, Mohd Tahir Ismail, Improving forecasting accuracy using quantile regression neural network combined with unrestricted mixed data sampling , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 5, Issue 4, November 2023
- Shaymaa Mohammed Ahmed, Majid Khan Majahar Ali, Raja Aqib Shamim, Integrating robust feature selection with deep learning for ultra-high-dimensional survival analysis in renal cell carcinoma , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- E. P. Onokare, L. O. Odokuma, F. D. Sikoki, B. M. Nziwu, P. O. Iniaghe, J. C. Ossai, Physicochemical Characteristics and Toxicity Studies of Crude Oil, Dispersant and Crude Oil-Dispersant Test Media to Marine Organisms , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 4, Issue 1, February 2022
- Santosh Kumar Upadhyay, Rajesh Prasad, Efficient-ViT B0Net: A high-performance light weight transformer for rice leaf disease recognition and classification , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 7, Issue 4, November 2025
- N. D. Umar, O. V. Omonona, C. O. Okogbue, Groundwater Quality Assessment Using Multivariate Analysis and Water Quality Index in some Saline Fields of Central Nigeria , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 4, November 2021
- Sylvester J. Gemanam, Nursakinah Suardi, Barnabas A. Ikyo, Samson Damilola Oluwafemi, Terver Daniel, Samuel T. Kungur, Biostimulation Effects and Temperature Variation in Stimulated Dielectric Substance (Diabetic Blood Comparable to Non-Diabetic Blood) Based on the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) in Laser Therapy , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 3, Issue 2, May 2021
- A. A. Ibiyemi, G. T. Yusuf, O. Akirinola, M. Orojo, B. Osuporu, J. Lawal, Investigating the magnetic domain structure and photonics characters of Singled Phased hard ferromagnetic Ferrite MFe3O4 (M= Co2+, Zn2+, Cd2+) Compounds , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 6, Issue 1, February 2024
- J. O. Coker, H. H. Akpan, A. O. Atilade, O. F. Ojo, Seasonal Comparison of Potential Groundwater Aquifer in Ijebu-Ife, South-West, Nigeria, using Dipole-Dipole Array and Electromagnetic Methods , Journal of the Nigerian Society of Physical Sciences: Volume 2, Issue 4, November 2020
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.






